Table of Contents
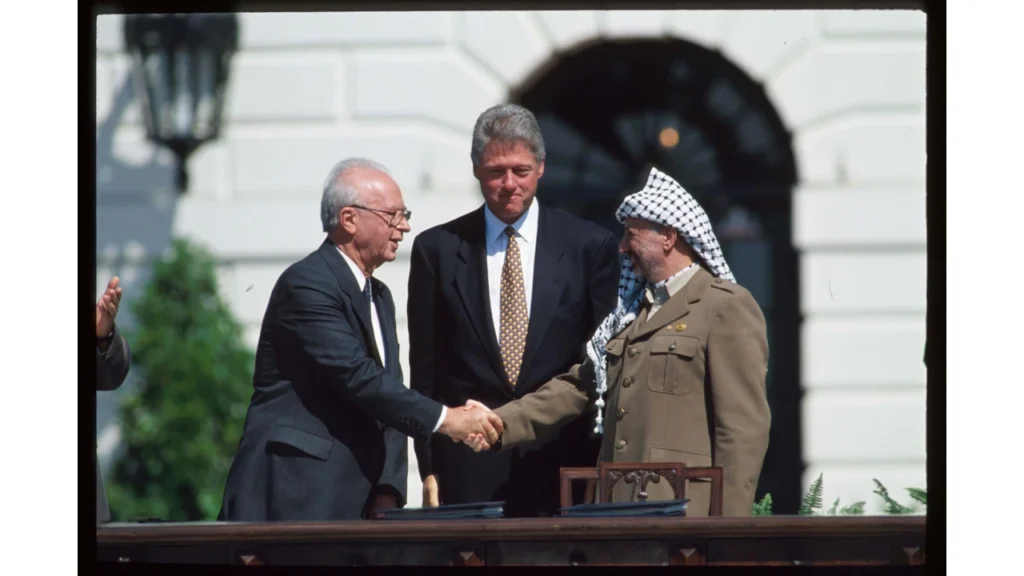
The North Atlantic Treaty Organisation, or NATO, is a military and political bloc that was set up in 1949. It was made so that its member states could work together to protect and defend themselves. At present, NATO has 31 member countries. These countries, called NATO Allies, are sovereign states that come together through NATO to discuss political and security issues and make collective decisions by consensus.
Over the years, It has played a big part in shaping geopolitics and making sure that the Trans-Atlantic area is safe and stable. This article gives an overview of NATO, including its background, structure, key principles, and how its role in global security has changed over time.
History
After World War II, the Soviet Union and the spread of communism were seen as a security threat, so NATO was created as a defense against them. In April 1949, when the North Atlantic Treaty was signed, it brought together the United States, Canada, and 10 European countries. Since then, 21 more countries have joined Alliance through nine rounds of enlargement (in 1952, 1955, 1982, 1999, 2004, 2009, 2017, 2020, and 2023).
Key Principles and Objectives
The main idea behind NATO is collective defence, government consultation, and cooperation. Article 5 is the most important part of the alliance. It says that an armed attack on one member is seen as an attack on all members and will be met with a group response.
NATO's main goals are to keep the peace, promote democratic ideals, and protect the territorial integrity of the countries that are members. It also wants to improve defence and security cooperation, improve the ability to handle crises and build partnerships with countries that are not members.
Structure and Decision-making
NATO is made up of “Civilian Structure“, “Military Structure“, and “Organisations and Agencies“. Consensus decision-making is a fundamental principle. It has been accepted as the sole basis for decision-making in NATO since the creation of the Alliance in 1949. The North Atlantic Council (NAC) oversees the political and military process relating to security issues affecting the whole Alliance.. The NAC is made up of representatives from each member country. The military structure of NATO is made up of different command structures and agencies that plan, coordinate, and carry out defence operations.

Evolution and Transformation
Since the end of the Cold War, NATO has changed a lot to keep up with new security threats. It has added countries from Central and Eastern Europe, including some that used to be in the Warsaw Pact. It has also been very important in many foreign operations, such as keeping the peace, fighting terrorism, and handling crises.
In the past few years, It has put more stress on collective defence and deterrence. This is because Russia and China has become more assertive, cyber threats have increased, and the Middle East has become less stable. The alliance has put money into improving its military skills, getting ready for battle, and building stronger relationships with other countries and groups.
NATO’s Engagements
Throughout its history, Alliance has been involved in several wars and armed actions. Here are some famous examples:
- Kosovo War : In 1999, during the Kosovo War, It launched a 78-day bombing campaign against the Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (i.e. Serbia and Montenegro) to stop the ethnic cleansing and violations of human rights in Kosovo. The operation, which was called “Operation Allied Force,” was NATO’s first big battle.
- Afghanistan Invasion: After the September 11 attacks in the United States, It used Article 5 for the first time to say that the attacks were an attack on all NATO countries. So, NATO led the International Security Assistance Force (ISAF) in Afghanistan to help stabilize the country, fight insurgency, and back the Afghan government. In 2015, ISAF became the Resolute Support Mission, whose main goal is to train, advise, and help Afghan security forces.
- Libya Intervention: NATO did a military operation in Libya in 2011 to protect people during the uprising against Colonel Muammar Gaddafi’s government. Operation “Unified Protector” meant putting in place a no-fly zone, putting in place an arms embargo, and bombing Gaddafi’s troops from the air.
- Operations against piracy: Since 2008, It has been working to stop piracy off the coast of Somalia. Operation “Ocean Shield” was run by NATO. Its goal was to stop and disrupt pirate operations and make sure that merchant ships in the area could travel safely. 2016 was the last year of the business.
- Support to Iraq (2018-present): It has helped the Iraqi security forces fight terrorists and keep the country stable by giving them training and advice. The goal of the NATO Training and Capacity Building Mission in Iraq is to make Iraq’s military institutions and defense assets better.
- Baltic Air Policing: It does air policing tasks in Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania to make sure their airspace is safe. Member states take turns sending out their fighter planes to keep air surveillance and response powers going all the time.
Challenges
The security situation of today presents NATO with several problems. Some of these are growing geopolitical tensions( Russia-Ukraine war ), terrorism, hybrid warfare, and the spread of weapons that can kill a lot of people. Also, member states have different views on some topics (Turkey’s objection to the inclusion of Sweden in NATO ), which makes it harder to reach a consensus and make decisions within the alliance.
Conclusion
Over the past seven decades, NATO has been a very important part of supporting peace, stability, and group defence among its member states. It has changed to deal with new security risks, and it will continue to do so. As the world’s security situation changes, NATO’s commitment to collective security is still important to protect the interests of its member countries and keep things stable in the Euro-Atlantic area and beyond.