Donald John Trump, born on June 14, 1946, is a prominent figure in American politics, media, and business. Serving as the 47th and current president of the United States since 2025, Donald Trump had earlier held office as the 45th president from 2017 to 2021, making him the second U.S. president after Grover Cleveland to serve non-consecutive terms. A staunch member of the Republican Party, Donald Trump political and personal trajectory has been one of significant controversy, innovation, and public scrutiny.
Donald Trump presidency 45th & 47th of the United States
Donald Trump graduated from the prestigious University of Pennsylvania in 1968 with a bachelor’s degree in economics. He inherited the Trump family real estate business in 1971, transforming it into a symbol of luxury and grandeur. Throughout the 1980s and 1990s, Trump expanded into high-profile construction projects, gaining fame for his opulent buildings and casinos. However, financial struggles followed, with multiple bankruptcies affecting his ventures in the 1990s.
Donald Trump victory in the 2016 presidential election marked a seismic shift in American politics. Running as a political outsider, he appealed to disenfranchised voters with his promises to “Make America Great Again.” His immigration policies dominated much of his early presidency, including a controversial travel ban targeting several Muslim-majority countries and an emphasis on expanding the U.S.–Mexico border wall. His administration also initiated a brief but widely criticized family separation policy for migrants.
On the domestic front, Donald Trump signed significant legislation such as the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017, which brought sweeping changes to the tax code. Internationally, his administration pursued a trade war with China, resulting in a dramatic impact on global markets. Donald Trump also withdrew the United States from pivotal agreements, including the Paris Climate Accord, the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (Iran nuclear deal), and the Trans-Pacific Partnership, citing national interest concerns.
Early Life and Education of Donald Trump presidency
He was the fourth child of Fred Trump, a successful real estate developer, and Mary Anne MacLeod Trump, a Scottish immigrant. Donald Trump ancestry is a blend of German (through his father) and Scottish (through his mother), reflecting a rich cultural heritage. Raised in the affluent Jamaica Estates neighborhood, he grew up with his siblings: Maryanne, Fred Jr., Elizabeth, and Robert. From an early age, Donald Trump family background gave him exposure to wealth, and by the time he was eight years old, he was a millionaire in 2024 dollars, benefiting from his father’s prosperous real estate empire.
Childhood, Personality, and Early Education
As a child, Donald Trump was known for his high energy and occasionally unruly behavior. He began his education at the Kew-Forest School, a private institution in Forest Hills, Queens. In addition to academics, he attended Sunday school at the First Presbyterian Church in Manhattan, reflecting his Presbyterian upbringing. However, his strong-willed and often difficult nature led his parents to make a pivotal decision regarding his education.
At the age of 13, Donald Trump presidency was enrolled in the New York Military Academy (NYMA), a private boarding school located north of New York City. The military-style environment of NYMA was intended to instill discipline and structure in his personality, and it proved formative in shaping his sense of confidence and leadership.
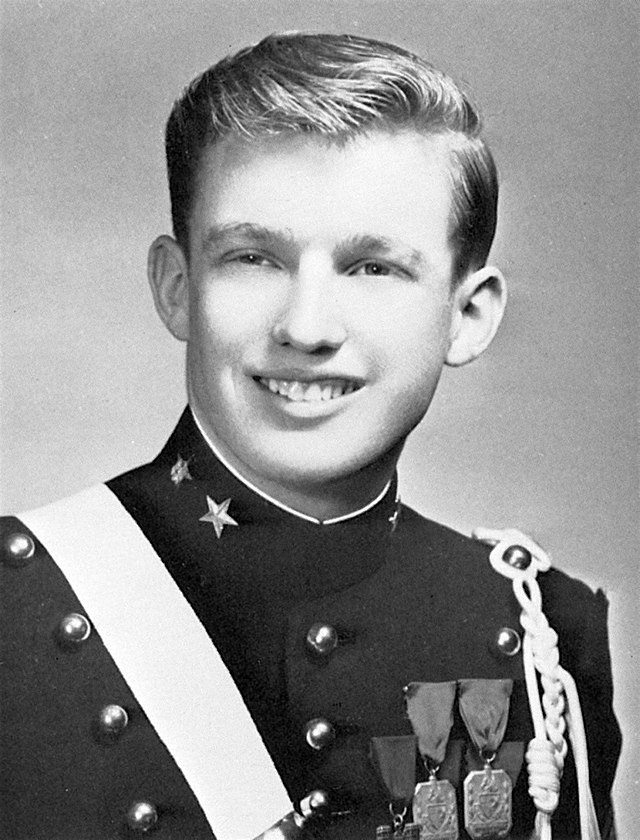

A notable photograph of Donald Trump during this period shows him as a teenager in his NYMA uniform, a visual reminder of the discipline and structure that marked his late childhood and adolescence. This time at NYMA gave Trump his first opportunity to engage in leadership roles and develop a commanding demeanor.
Higher Education and Career Aspirations
Donald Trump initially showed an interest in show business but eventually chose to follow in his father’s footsteps. In 1964, after completing his secondary education, he enrolled at Fordham University, a Jesuit institution in the Bronx. Seeking broader opportunities and inspired by his father’s business success, Donald Trump transferred two years later to the prestigious Wharton School of the University of Pennsylvania. At Wharton, he pursued a Bachelor of Science degree in economics, graduating in May 1968. Wharton was renowned for its rigorous business and finance programs, and Donald Trump education there further prepared him to take on the challenges of the real estate industry.
The Vietnam War Draft and Controversy
During this period, the Vietnam War was a central issue for young American men. Donald Trump received a draft deferment during his college years due to his education. After graduating, he was classified as medically unfit for military service due to bone spurs in his heels, an exemption that later drew significant public scrutiny. This aspect of his life would resurface decades later, fueling criticism from political opponents who questioned the legitimacy of his deferments.
Academic Record and Legal Threats
Donald Trump has long sought to control the narrative surrounding his academic performance. In 2015, as he prepared for his presidential run, he reportedly threatened legal action against his high school, colleges, and the College Board to prevent the release of his academic records. This move highlighted his emphasis on guarding his personal history and carefully shaping his public image.
The Foundation of Ambition
Donald Trump’s early life set the stage for his ambitious and often polarizing career. From his disciplined education at NYMA to his formal training in economics at Wharton, Donald Trump presidency cultivated the skills and personality traits that would define his ventures in real estate, television, and later, politics. These formative years, marked by privilege, controversy, and personal ambition, laid the groundwork for the dynamic and contentious figure he would become on the national stage. His story, deeply rooted in privilege and drive, is as much about early opportunities as it is about a fiercely individualistic vision for success.
Donald Trump’s Business Career: Real Estate, Challenges, and Controversies
Donald Trump’s journey in the world of business began in 1968, when he joined his father’s real estate company, Trump Management. The business primarily focused on owning and managing middle-class rental properties in New York City’s outer boroughs, which were often criticized for being racially segregated. By 1971, Donald Trump’s father appointed him as president of the company, marking the beginning of his leadership in transforming Donald Trump presidency Management into a brand-driven enterprise under the Trump Organization.
Early Legal and Ethical Challenges
Trump’s early years as president were not without controversy. In 1973, the U.S. government sued the company for its alleged racial discrimination against tenants. Trump, with the guidance of Roy Cohn, his influential lawyer and mentor, countersued the government for a staggering $100 million (equivalent to $686 million in today’s terms). Although the counterclaims were dismissed, the case ended with a consent decree mandating the desegregation of Trump properties. This incident underscored Donald Trump presidency aggressive legal tactics and refusal to concede without a fight.

Cohn, who had Mafia connections and played a key role in managing Trump’s projects, introduced him to Roger Stone, a political consultant. Stone became an essential ally in helping Donald Trump presidency navigate challenges with federal regulations. Despite the controversies, these connections solidified Trump’s reputation as a fearless, albeit controversial, dealmaker.
Financial Struggles and Bankruptcies
Between 1991 and 2009, six of Trump’s ventures filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy protection, reflecting the significant risks associated with his aggressive expansion strategy. These bankruptcies included prominent properties such as the Plaza Hotel in Manhattan and several casinos in Atlantic City, New Jersey. The recurring financial struggles painted a picture of a businessman willing to take on high-stakes ventures but not immune to failure.
In 1995, Trump defaulted on over $3 billion in loans, leading to a significant restructuring deal. Lenders seized the Plaza Hotel and other major properties but allowed Trump to avoid personal bankruptcy. This phase of his career was marked by a combination of resilience and vulnerability, with creditors believing that Donald Trump presidency public persona as a business magnate was too valuable to destroy.
Manhattan and Major Real Estate Projects
Trump’s foray into Manhattan real estate began in 1978 with the renovation of the Commodore Hotel, a project financed through a $400 million property tax abatement arranged by his father. The hotel reopened in 1980 as the Grand Hyatt Hotel, garnering widespread attention. This success paved the way for Donald Trump presidency most iconic development, Trump Tower, a mixed-use skyscraper in Midtown Manhattan that opened in 1983 and became both his company’s headquarters and his personal residence until 2019.
In 1988, Trump acquired the Plaza Hotel, which faced bankruptcy by 1992 due to unsustainable debts. While the reorganization plans allowed banks to take control, it further highlighted Donald Trump presidency precarious financial dealings. He later expanded his real estate footprint with the Trump Building at 40 Wall Street and the ambitious Riverside South project, where he eventually sold most of his interest to Asian investors to alleviate mounting debts.
In the early 2000s, Trump turned his attention to Chicago, where he developed the Trump International Hotel and Tower, a 92-story mixed-use skyscraper that opened in 2008. This project symbolized Trump’s persistence in high-profile construction ventures, despite financial challenges.
Allegations of Misconduct and Tax Controversies
Throughout his business career, Donald Trump presidency dealings were shrouded in allegations of misconduct. In 1992, he and his siblings formed All County Building Supply & Maintenance Corp., a company that reportedly served as a shell entity to inflate costs for Trump Management properties. This alleged scheme allowed the family to share profits from marked-up costs while seeking higher state-approved rent increases for their properties.
In 2024, investigative reports by the New York Times and ProPublica revealed that Trump was under Internal Revenue Service (IRS) scrutiny for potential tax fraud. He allegedly wrote off losses from cost overruns and unsold units in the Trump International Hotel and Tower in Chicago as worthless on his 2008 tax return. These allegations reignited debates about Donald Trump presidency financial integrity and business practices.
Despite his controversies and financial difficulties, Trump’s business ventures played a pivotal role in defining his image as a self-made billionaire and larger-than-life personality. His ability to recover from failures, maintain media attention, and leverage his brand for profitability established him as one of America’s most recognizable businessmen. However, his career remains a complex mix of ambitious achievements and ethically questionable practices. Donald Trump’s legacy in the real estate industry is as polarizing as his political career, reflecting a unique blend of audacity, resilience, and controversy.
Atlantic City Casinos: Bold Ambitions and Financial Struggles
Early Casino Projects
Donald Trump presidency opened his first casino in Atlantic City, Harrah’s at Trump Plaza, in 1984, with the assistance of Holiday Corporation for financing and management. However, the property struggled to generate profits, and by 1986, Trump paid Holiday Corporation $70 million to take full control of the casino.
In 1985, Trump acquired the unopened Atlantic City Hilton Hotel, which he renamed Trump Castle. Both Trump Plaza and Trump Castle were forced to file for Chapter 11 bankruptcy protection in 1992, reflecting ongoing challenges in making the properties financially sustainable.
Trump Taj Mahal: The Jewel and Its Downfall
In 1988, Trump purchased a third Atlantic City property, the Trump Taj Mahal. This ambitious casino project was financed using $675 million in junk bonds and completed at a total cost of $1.1 billion, opening its doors in April 1990. Dubbed the “eighth wonder of the world,” the Taj Mahal quickly became a symbol of Trump’s flamboyance and risk-taking.
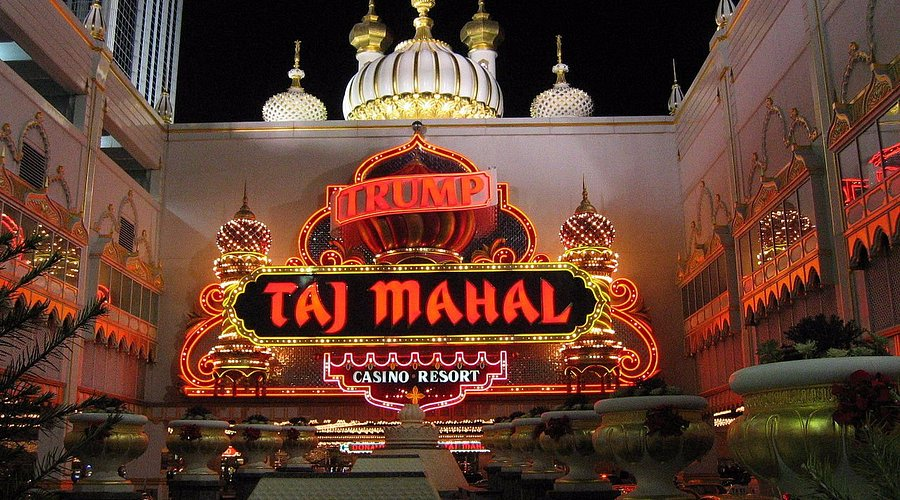

However, the casino’s high debt load led Trump to file for Chapter 11 bankruptcy protection by 1991, just a year after its grand opening. As part of the restructuring deal, Donald Trump presidency gave up half of his initial stake in the casino and personally guaranteed its future performance. To further address his $900 million in personal debt, Trump was forced to sell off key assets, including:
- Trump Shuttle, his airline service
- The Trump Princess, his luxurious mega yacht
- Other non-core businesses
Trump Hotels & Casino Resorts
In 1995, Donald Trump presidency consolidated his casino operations by founding Trump Hotels & Casino Resorts (THCR). This entity assumed ownership of the Trump Plaza and later acquired both the Trump Taj Mahal and Trump Castle in 1996. Despite these efforts to streamline operations, THCR faced substantial financial difficulties. It filed for bankruptcy twice, in 2004 and 2009, significantly reducing Donald Trump presidency ownership stake to just 10% by the time he stepped down as chairman in 2009.
The Mar-a-Lago Club and Golf Ventures
In 1985, Trump purchased the iconic Mar-a-Lago estate in Palm Beach, Florida. Originally a private residence, the sprawling property was transformed in 1995 into an exclusive private club with steep initiation fees and annual dues. Despite its commercial status, Trump retained a wing of the estate for personal use and officially declared it his primary residence in 2019.

Expanding his footprint in high-end leisure properties, Donald Trump presidency also turned to golf. Starting in 1999, the Trump Organization began acquiring and constructing luxury golf courses. Today, the company owns 14 Trump-branded courses and manages an additional three worldwide, making golf one of Trump’s most successful ventures in terms of global recognition.
Licensing the Trump Name
Over the years, the Trump name has become synonymous with luxury and ambition, leading to a lucrative business model of branding and licensing. The Donald Trump presidency Organization licensed his name for a wide variety of consumer goods and services, including:
- Apparel
- Home furnishings
- Food and beverages
- Learning courses
At its peak, the licensing strategy was a significant revenue generator. According to The Washington Post, Donald Trump presidency name had been used in over 50 licensing and management deals, producing at least $59 million for his companies. However, by 2018, following controversies surrounding his presidency, only two consumer goods companies continued to license the Trump name.
Donald Trump’s Side Ventures, Foundations, and Legal Controversies
Donald Trump’s diverse array of side ventures and businesses reveal both his entrepreneurial flair and his tendency to court controversy. From investments in sports and entertainment to high-profile legal disputes, Donald Trump presidency ventures have left a significant impact on multiple industries while often reflecting his risk-heavy approach to business.
Early Side Ventures: Sports and Entertainment
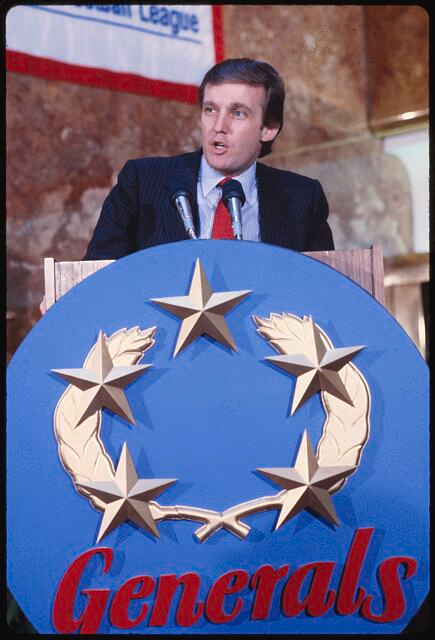
United States Football League (USFL) and the New Jersey Generals
In 1983, Trump acquired the New Jersey Generals, a team in the short-lived United States Football League (USFL). His tenure was marked by controversial decisions, including an unsuccessful push to shift the league’s schedule to fall, directly competing with the National Football League (NFL). This strategy, paired with an unsuccessful antitrust lawsuit aimed at forcing an NFL merger, contributed significantly to the league’s dissolution in 1985.
Boxing and the Tour de Trump
Trump and his Plaza Hotel frequently hosted boxing matches at the Atlantic City Convention Hall, cementing his involvement in sports promotions. In 1989, he launched the Tour de Trump, a cycling event modeled after the Tour de France. Despite generating interest as an American cycling spectacle, it only lasted two years.

Trump Shuttle
In 1988, Donald Trump presidency purchased Eastern Air Lines Shuttle for $380 million using bank loans. Renamed Trump Shuttle, it aimed to provide luxury airline services. However, mounting debts led to default on these loans in 1991, and ownership was handed over to banks.
Miss Universe and Hollywood Walk of Fame
In 1996, Trump purchased the Miss Universe Organization, which included the Miss USA and Miss Teen USA pageants. Trump’s management took the pageants to NBC in 2002, elevating their visibility. However, NBC and Univision severed ties with Donald Trump presidency in 2015 due to his remarks about Mexican immigrants. Trump’s involvement with Miss Universe earned him a Hollywood Walk of Fame star in 2007.
Controversies Surrounding Trump University
In 2005, Donald Trump presidency launched Trump University, a company offering seminars on real estate investing, charging up to $35,000 per course. Legal trouble began when New York State authorities ordered the company to cease using “university” in its name in 2010, leading to its rebranding as the Trump Entrepreneur Initiative.

By 2013, lawsuits from New York State and former students accused the company of deceptive practices, including false advertising and aggressive sales tactics. Internal documents revealed a hard-sell strategy targeting vulnerable consumers. Following his 2016 presidential victory, Trump settled three lawsuits for $25 million, avoiding further litigation.
The Donald J. Trump Foundation
The Donald J. Trump Foundation was founded in 1988, initially funded with Donald Trump presidency contributions. However, after 2006, most donations came from outside donors, including $5 million from Vince McMahon of WWE. The foundation supported charities linked to health, sports, and events at Trump properties.
In 2016, investigations revealed several violations, including self-dealing and failure to comply with state regulations. The New York attorney general filed a civil lawsuit in 2018, alleging misuse of funds. This led to the foundation’s closure and the disbursement of its remaining assets to other charities. In 2019, a judge ordered Trump to pay $2 million to charities for improper use of funds, some of which allegedly supported his political campaign.
Legal Affairs and Bankruptcies
A Legacy of Litigation
By 2018, Donald Trump presidency and his businesses were embroiled in over 4,000 state and federal lawsuits, ranging from contract disputes to allegations of fraud.
Corporate Bankruptcies
Although Donald Trump presidency himself never declared personal bankruptcy, his companies filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy protection six times between 1991 and 2009, including several of his Atlantic City casinos. Each restructuring aimed to address overwhelming debt while allowing continued operations.
Loss of Financial Backing
During the 1980s, Trump amassed significant loans, with over 70 banks lending $4 billion to fund his ventures. Following the corporate bankruptcies of the early 1990s, most banks, excluding Deutsche Bank, ceased lending to him. Even Deutsche Bank severed ties after the January 6 Capitol attack, citing reputational concerns.
A Complex Business Legacy
Donald Trump’s side ventures reveal a mix of ambitious successes and spectacular failures. From high-profile ventures like the USFL and Donald Trump presidency Shuttle to the legal controversies surrounding Trump University and his foundation, these endeavors illustrate his propensity to take risks, pursue media visibility, and push the limits of conventional business practices. While some ventures floundered, they collectively contributed to Trump’s identity as a polarizing yet influential figure in American business and culture.
Wealth of Donald Trump
Donald Trump has frequently claimed that his rise to wealth started with “a small loan of a million dollars” from his father, which he allegedly repaid with interest. However, records indicate that Donald Trump presidency borrowed at least $60 million from his father and largely did not repay these loans. Additionally, he inherited approximately $413 million (adjusted for inflation to 2018 dollars) from his father’s company, which served as a substantial foundation for his ventures.
A notable incident in Trump’s financial narrative occurred in 1984 when he, posing as a Trump Organization official named “John Barron,” contacted journalist Jonathan Greenberg. This move aimed to secure a higher ranking on the Forbes 400 list of America’s wealthiest individuals, illustrating Donald Trump presidency strategic approach to media representation of his wealth. Over the years, Trump has reported vastly varying figures regarding his net worth, spanning from minus $900 million in 1990 during financial difficulties to $10 billion in 2015, as per his personal estimations.
As of 2024, Donald Trump presidency financial status places him at $2.3 billion, ranking him 1,438th globally on the billionaires’ list. His ability to project an image of immense wealth has significantly influenced his brand, despite discrepancies in his financial narratives and reported net worth.
Media Career of Donald Trump
Donald Trump’s media presence has been instrumental in shaping his public image as a tycoon and entertainer. He has authored or coauthored 19 books, often with the assistance of ghostwriters. His debut book, “The Art of the Deal” (1987), became a New York Times Best Seller and was credited with establishing Trump as an emblem of business success. Ghostwriter Tony Schwartz, who is credited as a coauthor, played a pivotal role in bringing the book to life.
Trump’s media career extended beyond publishing. Between 1985 and 2001, he made numerous cameo appearances in films and television shows, building his persona as a celebrity businessman. In the 1990s, Donald Trump presidency became a recurring guest on the Howard Stern Show, appearing 24 times over the years. From 2004 to 2008, he hosted a short-form radio program, “Trumped!”, where he shared his opinions on various topics, further cementing his role as a public figure.
Between 2011 and 2015, Donald Trump presidency was a frequent commentator on the morning show Fox & Friends, a platform that amplified his visibility among a conservative audience. However, his media relationships faced a downturn following the January 6, 2021, attack on the U.S. Capitol. As a member of SAG-AFTRA since 1989, Trump resigned from the union in early 2021 to avoid disciplinary action related to his role in inciting the attack. Shortly afterward, the union took the rare step of permanently barring him, signaling a definitive end to his Hollywood affiliations.
Trump’s foray into media has not only bolstered his public image but also positioned him as a central figure in discussions of wealth, power, and influence, allowing him to transition seamlessly between the worlds of business, entertainment, and politics.
The Apprentice and The Celebrity Apprentice
Donald Trump’s television fame skyrocketed with The Apprentice and its variant, The Celebrity Apprentice, created by producer Mark Burnett. Donald Trump presidency not only hosted but also coproduced the shows, which aired from 2004 to 2015. In these programs, Trump played the role of a super-rich executive known for his catchphrase, “You’re fired,” as he eliminated contestants vying for business success.
The New York Times described Trump’s portrayal on the shows as “highly flattering and highly fictionalized.” However, this image of a powerful and successful business magnate resonated with millions of viewers nationwide, effectively reshaping his public persona. Through licensing agreements and show-related earnings, Trump amassed over $400 million, turning this media venture into a massive financial and branding success. The Apprentice and its spinoff significantly elevated Donald Trump presidency celebrity status, helping him transition from a businessman to a household name recognized across America.
Early Political Aspirations
Donald Trump’s engagement with politics dates back decades before his presidency. He initially registered as a Republican in 1987 but shifted his party affiliations multiple times—joining the Independence Party (an affiliate of the Reform Party) in 1999, the Democrats in 2001, and returning to the Republicans in 2009. By 2012, he reaffirmed his Republican alignment, solidifying his later political trajectory.
In 1987, Donald Trump presidency demonstrated his political ambition by placing full-page ads in prominent newspapers, outlining his ideas for foreign policy and strategies to tackle the federal budget deficit. A year later, in 1988, he approached Lee Atwater, the campaign strategist for George H. W. Bush, seeking consideration as Bush’s vice-presidential running mate. This request was deemed “strange and unbelievable” by Bush.
Donald Trump presidency briefly entered the 2000 Reform Party presidential primaries, campaigning for three months before withdrawing in February of that year. His political aspirations gained renewed attention in 2011 when he speculated about running against President Barack Obama in the 2012 election. Trump’s first significant political appearance occurred at the Conservative Political Action Conference (CPAC) in February 2011, followed by speeches in key early primary states. However, by May 2011, Trump announced he would not pursue the presidency.
At the time, Donald Trump presidency political ambitions were largely dismissed as theatrics, with many doubting his seriousness. Yet, his early forays into politics laid the groundwork for his eventual presidential run and his transformation into a key figure in modern American politics.
The 2016 Presidential Election
Donald Trump announced his candidacy for the presidency in June 2015. Although initially dismissed by political analysts, he quickly gained momentum, dominating opinion polls. By March 2016, Donald Trump presidency became the Republican front-runner and was officially declared the party’s presumptive nominee in May 2016. His provocative statements and media-savvy tactics granted him an unprecedented level of free coverage, allowing him to outshine more conventional competitors.
Donald Trump presidency campaign was characterized by his unconventional and often controversial rhetoric. He rejected political correctness and frequently alleged media bias, framing himself as a candidate for the average American. Despite the fact-checking community documenting a record number of his statements as false, his appeal grew. Trump’s campaign emphasized noninterventionist and protectionist views, calling NATO “obsolete” and promising renegotiation of trade agreements such as NAFTA to prioritize American interests.
Policy Priorities and Controversies
Central to Donald Trump presidency campaign was immigration reform, including a promise to build a border wall along the U.S.–Mexico border. He insisted that Mexico would finance the wall’s construction, while also advocating for strict enforcement of immigration laws and the deportation of millions of undocumented immigrants. Trump criticized birthright citizenship, claiming it incentivized so-called “anchor babies.” These views sparked widespread controversy and debates throughout the election season.
Donald Trump presidency pledged to enhance U.S.–China relations through renegotiated trade deals, focus on energy independence, and reduce taxes to simplify the tax code. He also proposed repealing the Affordable Care Act (ACA), modernizing veterans’ services, increasing military spending, and introducing tariffs to discourage outsourcing by American businesses. His proposed ban on immigrants from Muslim-majority countries and calls for “extreme vetting” further polarized public opinion.
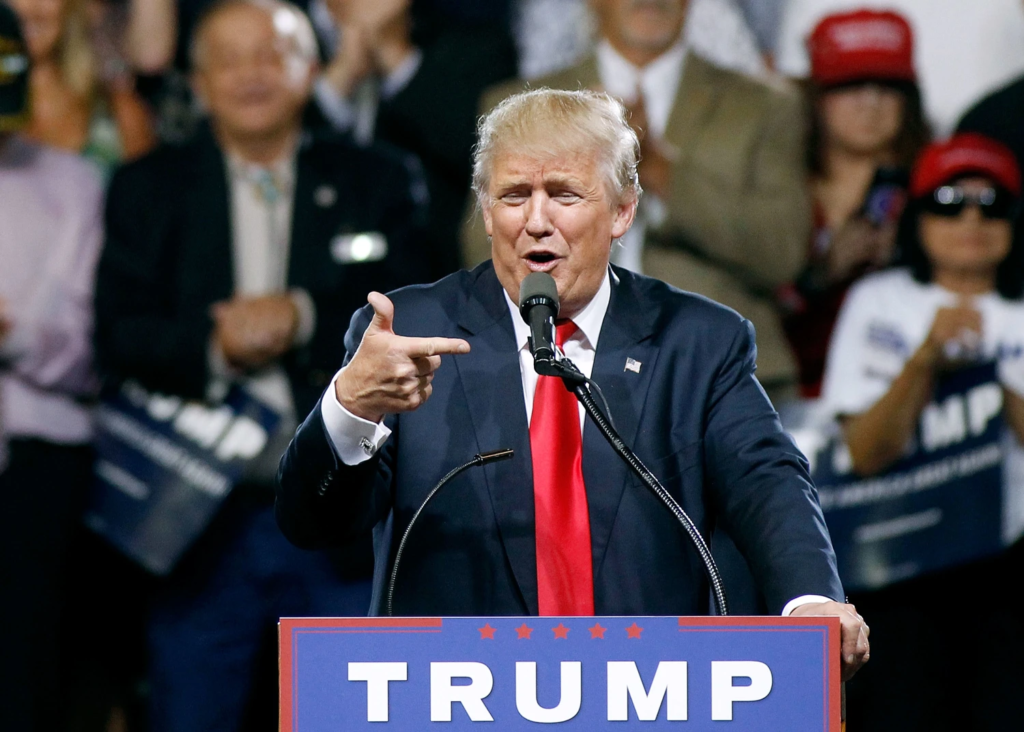

Critics often accused Donald Trump presidency of making racially charged statements to appeal to white voters. His controversial campaign launch included remarks about Mexican immigrants that drew backlash and cost him his contract with NBC, where he was fired from The Celebrity Apprentice.
Financial Disclosures and Tax Return Controversies
Donald Trump presidency financial disclosures, mandated by the FEC, reported assets exceeding $1.4 billion and debts of at least $315 million. However, he refused to release his tax returns, breaking a tradition followed by presidential candidates since 1976. Trump cited an ongoing IRS audit as his reason, despite legal experts suggesting the audit would not prevent disclosure. In 2021, after extensive litigation, the U.S. Supreme Court allowed the release of his financial records to prosecutors.
In October 2016, leaked tax filings revealed that Trump had declared a $916 million loss in 1995, potentially allowing him to avoid federal taxes for up to 18 years. This revelation added to the controversies surrounding his business practices and financial transparency.
Electoral Outcome
On November 8, 2016, Donald Trump presidency secured 304 electoral votes after defections, compared to 227 for Hillary Clinton. Although he lost the popular vote by 2.9 million votes—Clinton receiving 48.25% to Trump’s 46.3%—he became the fifth president to win the Electoral College while losing the popular vote.
Donald Trump presidency victory flipped traditionally Democratic strongholds such as Michigan, Pennsylvania, and Wisconsin, signaling the end of the so-called “blue wall.” With his victory, the Republican Party regained complete control of the federal government, holding the presidency alongside majorities in both chambers of Congress.
Despite his triumph, Donald Trump presidency election was met with massive protests across major U.S. cities, reflecting a deeply divided electorate. This unprecedented political ascent, as the first U.S. president with no prior government or military experience, underscored the disruptive impact of his campaign strategies and messaging.
First Presidency (2017–2021)
Donald Trump’s first term as president began with his inauguration on January 20, 2017. Just a day later, on January 21, an estimated 2.6 million people worldwide participated in the Women’s Marches to protest his presidency, with approximately half a million gathering in Washington, D.C. These marches were fueled by concerns over his stance on women’s rights, immigration, and other progressive policies.
Early Executive Actions
In his first days as president, Donald Trump presidency was highly proactive, signing six executive orders within his initial week in office. These included key actions such as:
- Initiating steps to dismantle the Affordable Care Act (“Obamacare”) and trigger its repeal process.
- Withdrawing from the Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP) trade negotiations.
- Reinstating the Mexico City policy, which restricted U.S. funding for foreign organizations that performed or provided information on abortions.
- Moving forward with controversial energy projects like the Keystone XL and Dakota Access pipelines.
- Increasing border security, which set the stage for his signature promise of building a wall along the U.S.–Mexico border.
In addition to these orders, Trump’s daughter Ivanka became a White House assistant, and his son-in-law Jared Kushner assumed the role of senior advisor.
Ethical Concerns and Conflicts of Interest
Trump’s business empire raised significant ethical concerns during his presidency, particularly around conflicts of interest. Ahead of his inauguration, Donald Trump presidency moved his extensive business interests into a revocable trust rather than a blind trust—a decision that was scrutinized for not severing ties cleanly between his presidential duties and his business ventures.
He continued to profit from the Donald Trump presidency Organization throughout his presidency, with significant financial gains tied to his hotels and resorts, particularly those in high-demand locations. His policies often reflected his personal business interests—the implications of this raised questions about the potential for foreign influence and personal financial gain.
Although he promised not to initiate new foreign deals, the Donald Trump presidency Organization expanded its operations globally, with notable ventures in Scotland, Dubai, and the Dominican Republic. These international expansions, alongside donations from lobbyists and foreign government officials, generated substantial profits for Trump’s business enterprises.
The potential violation of the U.S. Constitution’s Domestic and Foreign Emoluments Clauses became a matter of legal scrutiny. These clauses are intended to prevent U.S. officials from receiving gifts or payments from foreign governments without the approval of Congress. In 2017, Donald Trump presidency faced lawsuits accusing him of such violations. While lower courts dismissed one case, the U.S. Supreme Court deemed two others moot after he left office, indicating the complex intersection of business and governance during his administration.
Domestic Policy (2017–2021)
Donald Trump’s domestic policy in his first term was marked by key actions that sought to reshape the U.S. economy, environmental protections, social welfare, and other sectors, sparking significant debate and division.
Economic Policy
Donald Trump presidency entered office in January 2017 during the final year of the longest economic expansion in U.S. history, which had started in 2009. Despite this, one of the central focuses of his administration was economic growth and tax reform. The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017, signed into law in December of that year, was the hallmark of his domestic economic agenda. The act reduced tax rates for both businesses and individuals and effectively repealed the Affordable Care Act’s (ACA) individual mandate by setting the penalty to zero.
Donald Trump presidency argued that this reform would stimulate economic growth, but in 2018, government revenues were actually 7.6% lower than projected. While Trump emphasized tax cuts and deregulation as drivers of economic prosperity, his policies led to a significant increase in the federal deficit, which rose by nearly 50% to almost $1 trillion in 2019. Additionally, the U.S. national debt surged by 39%, reaching $27.75 trillion by the end of his term, and the debt-to-GDP ratio hit the highest post-World War II level. Moreover, Donald Trump presidency failed to implement the $1 trillion infrastructure spending plan he had promised during his campaign.
One significant aspect of the Donald Trump presidency was a decline in the labor force, with the U.S. workforce shrinking by 3 million people under his administration, marking him as the first modern president to leave office with a smaller workforce than when he took office.
Environmental Policy
Donald Trump presidency approach to environmental policy was centered on rolling back regulations and prioritizing fossil fuel production, diverging sharply from his predecessors. He consistently rejected the scientific consensus on climate change and reduced the budget for renewable energy research by 40%, while simultaneously pushing for the expansion of fossil fuels, particularly natural gas.
In a highly controversial move, Donald Trump presidency withdrew the U.S. from the Paris Climate Agreement in 2017, becoming the only country to opt out. His administration rolled back over 100 federal environmental regulations designed to tackle greenhouse gas emissions, air and water pollution, and the use of toxic substances. Furthermore, he weakened protections for animals and redefined environmental standards for federal infrastructure projects, including opening up parts of the Arctic National Wildlife Refuge for oil drilling.
Social and Health Policy
Trump’s domestic agenda was also defined by shifts in policy regarding healthcare, immigration, labor rights, LGBTQ+ rights, and more. During his first year, he made significant efforts to repeal the Affordable Care Act (ACA). However, his administration faced substantial legal opposition as it sought to undo aspects of the law, particularly around the individual mandate. In 2018, Donald Trump presidency joined with 18 Republican-led states in a legal bid to declare the entire ACA unconstitutional, but the courts did not support his attempt.
While campaigning, Trump promised to protect Medicare and other social safety-net programs, but in January 2020, he expressed openness to reducing their funding, drawing heavy criticism.
The opioid epidemic prompted a response from the Donald Trump presidency administration, with legislation passed in 2018 to allocate additional funding to drug treatment programs. However, he was criticized for the lack of a concrete strategy for effectively curbing the crisis.
Donald Trump presidency also took numerous actions related to social issues, including:
- Restricting federal funding for organizations that provide abortions or referrals.
- Attempting to undo Obama-era protections for LGBTQ+ individuals, including in the workplace and for transgender people.
- Continuing his stance against gun control, although his views on the issue evolved during his presidency.
- Holding an anti-marijuana position, reversing protections for states that had legalized cannabis.
In a more controversial aspect, Donald Trump presidency administration reinstated the federal practice of capital punishment. Under his leadership, the U.S. executed 13 prisoners—a stark contrast to the previous 56 years where the federal government had executed far fewer people. This policy decision sparked a broader debate over his administration’s approach to human rights and the criminal justice system.
Race Relations (2017–2021)
During his presidency, Donald Trump’s approach to race relations was highly contentious and often resulted in significant backlash. Several incidents and remarks during his time in office fueled accusations of racism, divisiveness, and polarization in the nation’s racial discourse.
Controversial Remarks and Actions
Donald Trump presidency faced sharp criticism for his response to the 2017 Unite the Right rally in Charlottesville, Virginia. After a violent confrontation between white supremacist groups and counter-protesters, Donald Trump presidency comments that there were “very fine people on both sides” were widely seen as an attempt to provide moral equivalence between the two opposing groups, effectively condoning the presence of neo-Nazis and white nationalists. Many perceived this as an endorsement of white supremacist ideology. His statement was seen as a stark contrast to the more standard condemnation of hate groups that many felt should have been emphasized in the wake of the violence.
In January 2018, Donald Trump presidency was reported to have made derogatory remarks during an immigration meeting, calling El Salvador, Haiti, Honduras, and African nations as “shithole countries.” These remarks were widely condemned across both sides of the political spectrum as racist and inflammatory, further drawing attention to his polarizing language on immigration and race.
Later, in July 2019, Donald Trump presidency stirred further controversy by tweeting those four minority Democratic congresswomen—three of whom were U.S.-born—should “go back” to the countries from which they “came.” The comments were widely criticized as racially charged and xenophobic. The House of Representatives voted to condemn the comments as racist in a 240–187 vote. These remarks were seen as part of a broader narrative were Donald Trump presidency comments consistently provoked allegations of racist language and sentiment, especially targeting people of color.
George Floyd Protests and Response
The George Floyd protests in 2020 marked a pivotal moment in Donald Trump presidency relationship with race relations. The protests, sparked by Floyd’s death at the hands of a white police officer in Minneapolis, led to widespread demonstrations across the country demanding racial justice and police reform. In response to the protests, particularly those that occurred outside the White House, Trump employed a highly controversial response: federal law enforcement officials removed peaceful protesters from Lafayette Square to allow for a photo opportunity in front of St. John’s Episcopal Church, where Donald Trump presidency was seen holding a Bible.
This moment quickly sparked outrage among religious leaders, military veterans, and human rights activists. Many viewed it as an improper use of government force to clear peaceful demonstrators for a personal and political photo-op. Donald Trump presidency approval for a strong federal response to the protests also faced heavy criticism from former military leaders and defense officials who warned against deploying the U.S. military against anti-police brutality protesters. Ultimately, Donald Trump presidency handling of the protests was seen as exacerbating racial tensions in the country, rather than addressing the core issues related to police violence and racial inequality.
Pardons and Clemency
In the final days of his presidency, Donald Trump presidency made the decision to grant pardons and commutations to many individuals, drawing mixed reactions. While some celebrated these actions, others raised concerns about the influence of personal connections and political alliances in the selection of recipients. Among the 237 clemencies granted during his presidency, a significant number were individuals with personal ties to Donald Trump presidency, his family, or his allies. This led to allegations of favoritism, with claims that clemency was at times given to those with personal connections or celebrity endorsements.
Criticism also emerged over the pardons granted to military service members convicted of violent crimes. These decisions, which included pardons for service members convicted of war crimes—in opposition to the military leadership’s recommendations—raised serious questions about Donald Trump presidency position on military ethics and his readiness to shield people close to him from legal consequences.
Immigration Policy
Immigration was one of the most divisive issues during Donald Trump presidency. Frequently labeling illegal immigration an “invasion”, Donald Trump presidency described migrants from Central America and elsewhere as a threat, specifically linking them with criminal organizations such as MS-13. His approach to immigration enforcement became more aggressive, with large-scale deployments of U.S. military troops to the southern border to stop migration and asylum seeking from Central America. By 2018, Donald Trump presidency had deployed nearly 6,000 troops in what was seen as an overreaching measure against asylum seekers.
His administration’s stance on refugees became a central issue as well. Upon entering office, the U.S. was admitting up to 110,000 refugees per year. However, Donald Trump presidency significantly reduced this limit, slashing the number to a record-low 18,000 in 2020 and further cutting it to 15,000 in 2021. His efforts to restrict refugee admissions and tighten immigration policies faced sustained opposition from immigrant rights groups and international bodies that criticized the drastic reduction of legal avenues for resettling refugees.
Donald Trump presidency also implemented additional policies such as the public charge rule, which made it harder for immigrants who might require public assistance to gain permanent residency. This was seen as a direct attack on low-income immigrants, many of whom come from racially marginalized groups.
Travel Ban and Immigration Policy
Trump’s Travel Ban became one of his most controversial and widely debated policies. The policy first took shape when he signed Executive Order 13769 on January 27, 2017, which suspended the admission of refugees for 120 days and imposed a 90-day travel ban on citizens from Iraq, Iran, Libya, Somalia, Sudan, Syria, and Yemen due to alleged national security concerns. The immediate execution of the order led to chaos at U.S. airports, with protests erupting almost instantly.
Legal challenges quickly followed, leading to preliminary injunctions being issued across the country. A revised version of the order was signed in March 2017, which removed Iraq from the list of banned countries and included certain exemptions for green card holders and visa holders. However, federal judges from three states blocked this version as well.
In June 2017, the U.S. Supreme Court allowed a limited version of the travel ban to take effect for travelers without a “credible claim of a bona fide relationship” with U.S. persons or entities. Eventually, on September 24, 2017, Presidential Proclamation 9645 was implemented, expanding the ban to include North Korea, Chad, and certain Venezuelan officials. The travel restrictions were modified multiple times, and in June 2019, the Supreme Court ruled to uphold the ban, despite continued legal opposition and widespread protests, ensuring its full enforcement.
Family Separation at the Border
The family separation policy introduced by the Donald Trump presidency administration sparked widespread national outrage. In 2017 and 2018, the administration implemented a “zero tolerance” policy at the U.S.–Mexico border, which resulted in over 5,400 children being separated from their migrant families. The policy aimed to criminally prosecute every adult caught crossing the border illegally, effectively splitting families.
This decision was unprecedented and garnered fierce backlash, as it seemed inhumane and in violation of basic human rights. Donald Trump presidency initially tried to deflect responsibility for the policy, claiming the separations were a necessary result of existing laws, despite the policy being an initiative of his own administration. Amid the outcry, he reluctantly signed an executive order in June 2018 to end the separations, though by then, more than a thousand children had already been separated.
Legal actions culminated in Judge Dana Sabraw ordering the administration to reunite families and stop further separations, except in specific circumstances. Even after this ruling, the administration continued the practice for a period, and the American Civil Liberties Union (ACLU) raised concerns over the lack of systems to track separated families, exacerbating the humanitarian crisis.
Mexico–United States Border Wall and Government Shutdown
One of Donald Trump presidency signature campaign promises was the construction of a border wall to prevent illegal immigration, specifically to reduce border crossings from Mexico. By the end of his presidency, only a fraction of the wall was constructed—365 miles of primary and secondary barriers, far less than the 1,000 miles initially promised. His administration did manage to build new primary walls and replace outdated fencing in various locations along the southern border.
A major political impasse over funding for the wall led to a 35-day government shutdown between December 2018 and January 2019, the longest in U.S. history. Trump insisted on allocating $5.6 billion for the wall, but Congress refused. This deadlock led to massive disruptions in government operations, with approximately 800,000 government workers furloughed or working without pay, costing the U.S. economy around $3 billion in lost productivity.
The shutdown ended when a temporary funding agreement was reached, providing delayed payments for government workers, but the border wall was not funded. In February 2019, Donald Trump presidency accepted a bill offering $1.375 billion for 55 miles of border fencing but declared a national emergency to divert additional funds for the wall. This controversial move faced legal challenges, but the courts ruled in Donald Trump presidency favor, allowing him to repurpose funds designated for military construction and anti-drug measures. The attempt to use military funds was strongly contested but ultimately went forward, with the legal battles continuing over the use of these reallocated resources.
Foreign Policy Under Donald Trump
Donald Trump’s foreign policy was characterized by a mix of unpredictability, populist nationalism, and a strong focus on “America First” rhetoric. He positioned himself as a nationalist and often prioritized the U.S.’s direct interests in its global dealings, with a particular focus on trade policies and military engagements. His foreign relations were marked by strained alliances, controversial decisions, and inconsistent approaches across regions.
Trade Policies and Global Economic Relations
Under Donald Trump presidency, his trade policies were dominated by a desire to reduce U.S. trade deficits, implement more protectionist measures, and challenge what he perceived as unfair trading practices by foreign nations. One of his signature moves was withdrawing the U.S. from the Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP), a major multilateral trade agreement involving 11 Pacific Rim countries, including Japan, Canada, and Australia.
Donald Trump presidency trade war with China was another central issue. In 2018, he initiated a series of tariffs on Chinese goods, which grew into a comprehensive trade conflict involving more than $50 billion worth of Chinese imports. These tariffs, intended to force China to change its economic practices, were criticized because American companies bore much of the cost, despite Donald Trump presidency claim that China would pay. His administration eventually reached a Phase One Trade Agreement with China in 2020, which involved concessions on intellectual property and agricultural exports but left many issues unresolved.
The renegotiation of NAFTA led to the creation of the U.S.-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA), replacing the older trade deal in 2020. Donald Trump presidency claimed it was a major achievement for American workers, but critics noted the long-term effects remained to be fully seen.
Relations with Russia
Donald Trump presidency approach to Russia and Vladimir Putin was one of the most controversial aspects of his foreign policy. Donald Trump presidency expressed admiration for Putin and frequently praised his leadership style, drawing sharp criticism from both sides of the aisle. Critics argued that he was too lenient on Russia, particularly in regard to its actions in Ukraine and its 2016 election interference. Despite imposing sanctions on Russia over its annexation of Crimea, Donald Trump presidency seemed to favor a cooperative stance, proposing Russia’s potential re-entry into the G7 and frequently questioning the effectiveness of NATO, an alliance that Russia views as a rival.

Donald Trump presidency infamous 2018 meeting with Putin in Helsinki, where he appeared to accept Putin’s denial of election interference over the conclusions of U.S. intelligence agencies, deepened skepticism about his relationship with Moscow. His foreign policy toward Russia remained inconsistent but was marked by periods of cooperative rhetoric alongside moments of confrontation.
Engagement with East Asia: China, North Korea, and Taiwan
China was at the forefront of Donald Trump presidency East Asia policy, with his administration accusing China of being a currency manipulator, engaging in unfair trade practices, and cracking down on political dissidents. Donald Trump presidency aggressive rhetoric against Beijing included imposing tariffs and sanctions, particularly on Chinese tech company Huawei over concerns of espionage. Donald Trump presidency also took an assertive stance against China’s handling of the COVID-19 pandemic, which initially had positive comments from him, but later turned into sharp criticism as the virus spread globally.
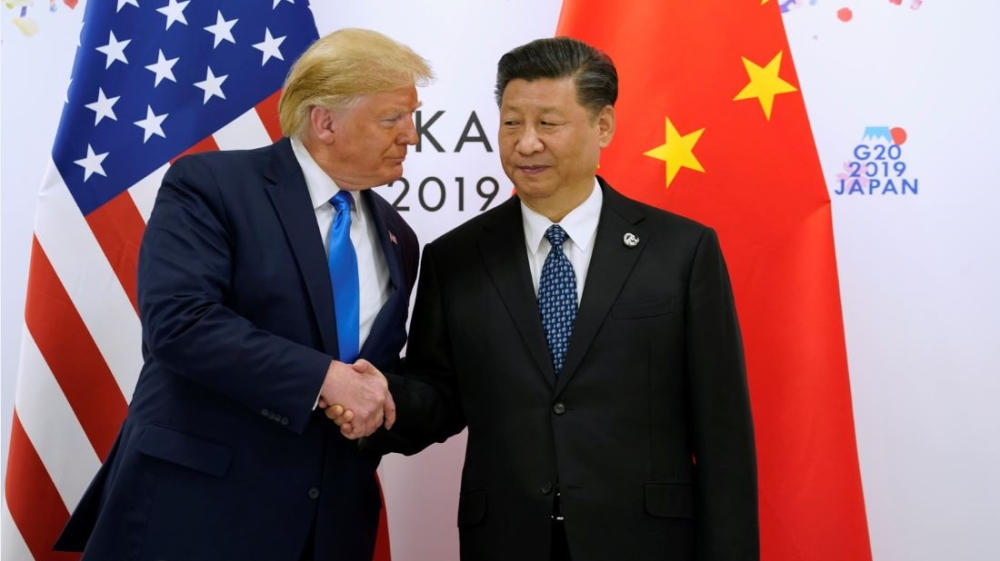

Despite this confrontation, Trump held a complex relationship with Chinese President Xi Jinping. He praised Xi as a leader during the trade talks, but also took a tough stance on other issues, such as Xinjiang where China faced accusations of ethnic persecution. In 2020, Donald Trump presidency sanctioned Chinese officials in response to the mass detentions of Uyghur Muslims, which significantly raised tensions between the two nations.
Trump’s stance on North Korea also received mixed reactions. Initially adopting combative rhetoric, such as threats of “fire and fury,” Trump later sought direct engagement with North Korean leader Kim Jong Un. He held three summits with Kim, marking a historic shift in U.S.-North Korea relations, but denuclearization talks ultimately stalled, and North Korea’s weapons programs continued. Trump’s bold claim of wanting complete denuclearization was undermined by the lack of a meaningful agreement during the summits. Nonetheless, he became the first sitting U.S. president to meet a North Korean leader, which was portrayed as a breakthrough in diplomacy despite limited tangible progress.
North America and U.S. Border Security
Trump’s foreign policy also prominently featured efforts to strengthen U.S. border security, which was a cornerstone of his political platform. His administration pushed for a border wall between the U.S. and Mexico as part of a broader strategy to curb illegal immigration. Although progress on the border wall was slow, funding issues caused a 35-day government shutdown in late 2018 and early 2019, as Trump insisted Congress allocate billions of dollars for the project.

His aggressive stance on border security led to policies such as family separations, which drew widespread condemnation. The “zero tolerance” policy resulted in more than 5,000 children being separated from their migrant families at the U.S.-Mexico border, a decision Trump later rescinded in the face of public outrage.
Donald Trump’s foreign policy focused on a combination of assertive nationalism, shifting U.S. alliances, and military intervention. This policy had significant consequences, particularly in the Middle East.
Afghanistan
Trump’s approach to Afghanistan evolved during his presidency. Initially, he criticized the war, but by 2018, U.S. troop numbers increased from 8,500 to 14,000. However, in February 2020, the Trump administration signed the U.S.-Taliban agreement, promising the withdrawal of U.S. troops within 14 months, contingent on the Taliban’s agreement not to harbor terrorists. By the end of Trump’s presidency, 5,000 Taliban prisoners were released, and troop numbers had reduced to 2,500, even as the Taliban continued their attacks.
Israel
Trump strongly supported Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu, backing policies such as recognizing Jerusalem as Israel’s capital and Israeli sovereignty over the Golan Heights, actions which were heavily criticized by many international bodies. In 2020, the signing of the Abraham Accords, normalizing relations between Israel, the United Arab Emirates, and Bahrain, was touted as a significant diplomatic achievement.
Saudi Arabia
Trump maintained close relations with Saudi Arabia, supporting their intervention in Yemen and agreeing to a $110 billion arms deal in 2017. After the 2019 attacks on Saudi oil facilities, which were attributed to Iran, the U.S. deployed additional troops to the region, signaling continued American support for Saudi defense.
Syria
In Syria, Trump ordered missile strikes against the Assad regime in retaliation for chemical weapon attacks. However, in 2018, Trump declared ISIS defeated, deciding to withdraw U.S. forces from the country. This move led to conflict with U.S. allies in the region, especially the Kurdish forces who had been instrumental in fighting ISIS, and gave rise to Turkish military action in northern Syria. Despite some successes, Trump’s decisions on Syria and his treatment of Kurdish allies were contentious and widely criticized by both Democrats and Republicans.
Iran
Trump’s relationship with Iran was marked by sharp escalation. In 2018, he withdrew the U.S. from the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (the nuclear deal), aiming to curb Iran’s nuclear ambitions. He also ordered the assassination of Qasem Soleimani, a senior Iranian general, in early 2020. Iran retaliated with missile strikes, and this marked a significant escalation between the two nations.
Personnel and Governance
The Trump administration saw unusually high turnover, especially among senior staff. Key officials, including National Security Advisor Michael Flynn, FBI Director James Comey, and various cabinet members, were either pushed out or resigned. Trump’s governance style contributed to a lack of consistency and public instability.
Judicial Appointments
Trump made a lasting impact on the U.S. judiciary, appointing 226 federal judges, including three Supreme Court justices: Neil Gorsuch, Brett Kavanaugh, and Amy Coney Barrett. His judicial appointees played a pivotal role in shifting the Court to the right, notably in the Dobbs v. Jackson Women’s Health Organization decision, which overturned Roe v. Wade.
Overall, Trump’s foreign and domestic policies emphasized American interests, often at the expense of multilateral cooperation, resulting in both victories and controversial decisions on the global stage.
Pressure to Abandon Pandemic Mitigation Measures
As the COVID-19 pandemic escalated in the United States, pressure mounted for the U.S. government to relax mitigation measures such as lockdowns and social distancing. Republican-connected groups organized anti-lockdown protests throughout the spring of 2020, arguing that restrictions on businesses and public activities were harming the economy. President Trump, who had initially downplayed the seriousness of the virus, supported these protests publicly, even while the targeted states did not meet the guidelines for reopening established by his administration. His messaging became increasingly conflicting, as he oscillated between endorsing states reopening early and expressing concern about their measures.
One significant incident occurred with Georgia Governor Brian Kemp, who, in April 2020, announced his intention to allow the reopening of nonessential businesses, even though his state was not prepared with sufficient testing or other safety protocols. Initially, Trump supported the decision but later criticized it. As the pandemic spread, Trump became more focused on ending restrictions, driven by concerns over the growing damage to the economy, which became a central issue for his political platform.
At public events, Trump often refused to wear a mask, despite guidelines issued by his administration to encourage mask-wearing in public to reduce virus transmission. This contradiction between Trump’s actions and medical recommendations, especially amid near universal consensus from healthcare professionals that masks were vital in preventing the spread of the virus, weakened national efforts to mitigate the crisis.
Testing and Political Interference
Trump’s comments regarding COVID-19 testing added further complications to the national response. In June and July, Trump made repeated claims that the U.S. would have fewer confirmed cases of COVID-19 if there were less testing. According to this rhetoric, the increase in reported cases made the country look bad on a global scale. This stance contradicted the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) guideline that asymptomatic individuals who were exposed to COVID-19 should still get tested to limit spread, even though they showed no symptoms.
In August 2020, Trump’s influence over the CDC led to political appointees pushing for changes to the agency’s testing recommendations. The CDC altered its guidance to suggest that people exposed to the virus but showing no symptoms did not necessarily need a test. This controversial revision led to accusations of political interference, as health experts within the agency, and outside, pushed back. Within days, the recommendation was reversed, although the damage to public trust was already significant.
Political Pressure on Health Agencies
Trump’s pressure on federal health agencies was not limited to testing and quarantine strategies. He sought to fast-track the development of vaccines and treatments for COVID-19 in a bid to mitigate the crisis. He pushed for the approval of unproven drugs, like hydroxychloroquine, while casting doubt on public health experts’ opinions. In his statements, Trump implied that scientists at the FDA were working against him, creating a narrative that some members of the “deep state” were undermining his political agenda. These actions undermined public trust in scientific agencies at a critical time, and many accused the Trump administration of sacrificing the integrity of scientific decision-making for political expediency.
White House COVID-19 Outbreak
The COVID-19 pandemic’s impact came very close to the heart of the U.S. government with the White House outbreak in October 2020. Trump himself tested positive for the virus on October 2, 2020, following an outbreak in the White House that also affected many staff members. Trump’s public handling of the situation, where he was admitted to Walter Reed National Military Medical Center for treatment but returned to the White House just days later, still contagious and visibly unwell, raised questions about the severity of his illness and his efforts to downplay the pandemic’s true impact.
Despite his illness, Trump continued to minimize the risk of the virus and did not revise his stance on the importance of restrictive measures like mask-wearing or maintaining other public health safeguards. Reports of Trump’s health status during his treatment indicated that he had suffered dangerously low blood oxygen levels, which would have suggested a far more serious illness than was publicly acknowledged by his administration at the time.
2020 Presidential Campaign and Pandemic Handling
As the 2020 presidential election approached, Trump’s handling of the pandemic became a critical issue. Democratic nominee Joe Biden framed the pandemic as a failure of leadership under Trump’s presidency. Polls indicated that voters disapproved of how Trump managed the pandemic, with the Ipsos/ABC News poll showing that 65% of respondents disapproved of his pandemic response. Despite this, Trump continued to claim that the pandemic was “under control”, downplaying rising case counts and deaths. His comments, like suggesting that 99% of COVID-19 cases were “totally harmless,” made it clear that his priorities centered more on the economy and re-election than on managing the public health emergency effectively.
As the pandemic continued throughout the year, the coronavirus became a driving issue in the 2020 election, contributing to increasing doubts about Trump’s leadership capabilities. On the eve of the election, the U.S. reached a grim milestone of 100,000 reported daily cases, illustrating the severity of the crisis under his watch.
Investigations into Trump’s Administration
Beyond his handling of the pandemic, Trump’s financial and personal conduct throughout his presidency led to investigations into multiple aspects of his private businesses and governmental actions. From tax investigations to potential interference with investigations into the pandemic and election processes, these inquiries sought to hold him accountable for decisions made in office. The Justice Department and Congress engaged in numerous investigations throughout Trump’s presidency, covering both his actions as president and his personal finances, potentially exposing conflicts of interest or illegal conduct.
The full scope of these investigations, which included issues related to the finances of the Trump Organization, remained ongoing during and after his presidency, ensuring that legal scrutiny over his administration’s actions would remain a significant part of his political legacy. The fact that financial and personal actions of a sitting president were subject to scrutiny demonstrated an enduring aspect of Trump’s controversial presidency—his constant confrontation with legal and political oversight.
Intelligence Confirmation of Russian Interference
In January 2017, U.S. intelligence agencies (CIA, FBI, and NSA) collectively stated with “high confidence” that the Russian government had interfered in the 2016 presidential election to help elect Donald Trump. The interference took many forms, including hacking and releasing Democrat-related emails, spreading disinformation through social media, and attempting to undermine Hillary Clinton’s campaign. The assessment was reinforced by a classified report shared with Congress and made public, marking the beginning of a broader inquiry into foreign influence in U.S. elections.
- Main Findings: The Russian government orchestrated a cyber-attack on the Democratic National Committee (DNC) to steal and leak emails to damage Clinton’s bid for presidency. They also used state-controlled media outlets like RT and Sputnik to spread favorable narratives about Trump.
- Intelligence Agencies’ Consensus: CIA, FBI, and NSA all had independent reports linking Russia’s efforts directly to the highest levels of the Russian government, including President Vladimir Putin, who was seen as being personally involved in directing these efforts.
Connections Between Trump Associates and Russia
As the investigation unfolded, numerous links between Trump’s campaign associates and Russian officials were unearthed. Some prominent individuals involved included Paul Manafort, Michael Flynn, Roger Stone, and George Papadopoulos. Their meetings and communications with Russian officials were a key focus of investigations.
- Paul Manafort: Trump’s campaign manager, Manafort, had extensive business ties to pro-Russian Ukrainian figures, and he was accused of sharing campaign strategy information with Russian intermediaries during the election. He was later convicted on multiple counts of financial crimes related to his work with Russian-aligned interests.
- Michael Flynn: Trump’s National Security Advisor, Flynn, was forced to resign after it was revealed that he had discussed U.S. sanctions with Russian Ambassador Sergey Kislyak before Trump took office. Flynn pleaded guilty to lying to the FBI about these contacts.
- Roger Stone: An associate of Trump’s from his business career, Stone was connected to efforts to gather and release politically damaging information. His involvement with WikiLeaks and attempts to gain access to the DNC’s stolen emails resulted in his criminal conviction for obstruction and witness tampering.
- Other Contacts: Several other members of Trump’s team, including Jared Kushner and Jeff Sessions, had interactions with Russian figures that were scrutinized, raising further questions about potential coordination.
The Mueller Investigation
In May 2017, following increasing political pressure, the Department of Justice appointed former FBI Director Robert Mueller as special counsel to lead an independent investigation into Russian interference in the 2016 election. Mueller’s investigation, known as the Mueller Probe, had several specific mandates:
- Links to Russia: To investigate possible coordination between the Trump campaign and Russia. This included whether the campaign received or solicited assistance from Russia in the election.
- Obstruction of Justice: To examine if President Trump attempted to obstruct justice, particularly surrounding his firing of FBI Director James Comey.
- Trump’s Personal and Business Ties: The probe looked into Trump’s personal, financial, and business dealings with Russia and foreign entities.
Findings:
- The investigation did not establish that Trump’s campaign conspired with Russia to affect the election results. Despite this, numerous links were discovered between campaign officials and Russian contacts.
- The report did find that Trump and his associates welcomed Russia’s interference and believed it would benefit their campaign. Evidence was found that showed Russian officials had a preference for Trump over Clinton and exploited social media to amplify divisive issues.
Obstruction of Justice
One of the key components of the Mueller investigation was to determine if President Trump tried to interfere with the investigation, obstructing justice. The Mueller report outlined several actions by Trump that raised questions about whether his efforts amounted to obstruction.
- Firing James Comey: Trump’s decision to dismiss FBI Director James Comey in 2017 was seen as part of an attempt to curtail the investigation into Russia’s interference. He later admitted he fired Comey partly because of the Russia investigation.
- Pressure on Witnesses: Trump took actions that could be viewed as attempts to intimidate or manipulate witnesses. This included efforts to discourage cooperation with Mueller’s investigation or pressuring officials to make statements favorable to him.
- Presidential Immunity: A critical aspect of the investigation was whether a sitting president could be indicted. The Department of Justice’s Office of Legal Counsel had issued an opinion stating that a sitting president could not be indicted, a legal opinion that affected how the investigation proceeded.
The report did not make a final determination on whether these actions amounted to obstruction because it could not definitively conclude that Trump had committed a crime, in part due to the inability to indict a sitting president.
Political Fallout
The outcome of the Mueller investigation had major political repercussions:
- Public Opinion: After the release of the Mueller report, Trump and his supporters claimed victory, insisting that the investigation was a witch hunt that proved he had no collusion with Russia. However, the report left lingering questions, particularly concerning obstruction, that continued to dominate the political discourse.
- Impeachment Inquiry: In 2019, following the Trump–Ukraine scandal, the House of Representatives opened an impeachment inquiry. Although the investigation uncovered serious questions about Trump’s behavior, no article of impeachment related to Russian interference was pursued, leaving his actions surrounding the Mueller investigation largely unresolved in Congress.
- Convictions and Guilty Pleas: A number of Trump’s associates were convicted or pled guilty to charges uncovered by the investigation. These included:
- Paul Manafort, convicted of financial crimes tied to his work with pro-Russian figures.
- Michael Flynn pled guilty to lying to federal agents.
- Roger Stone, convicted of witness tampering and obstruction.
- Michael Cohen, Trump’s former personal lawyer, who admitted to lying about the timing of a planned deal to build a Trump Tower in Moscow.
- Legal Consequences for Trump: While Trump himself was not charged, his associates’ convictions were a constant reminder of the ties between his campaign and Russian interests, leading to persistent legal and political pressure. Moreover, it raised doubts about his campaign’s transparency and trustworthiness.
First Impeachment: Trump–Ukraine Scandal
Whistleblower Complaint
In August 2019, a whistleblower filed a complaint regarding a July 25, 2019, phone call between President Trump and Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy. According to the complaint, Trump exerted pressure on Zelenskyy to investigate CrowdStrike, a cybersecurity firm, and Joe Biden—specifically Biden’s role in the firing of a Ukrainian prosecutor, a move which many saw as politically motivated. Trump also urged Zelenskyy to investigate Biden’s son, Hunter Biden, who had served on the board of a Ukrainian gas company, Burisma.
- Cover-up Allegations: The whistleblower alleged that the White House had attempted to cover up the call and that the President’s actions were part of a broader campaign orchestrated by Trump’s personal lawyer Rudy Giuliani. This alleged campaign may have included withholding U.S. military aid to Ukraine and attempting to influence Ukraine’s internal political issues for Trump’s benefit.
Pelosi’s Impeachment Inquiry
House Speaker Nancy Pelosi formally launched an impeachment inquiry in September 2019. Key points during this period included:
- Trump’s Admission: Trump admitted that he had withheld military aid to Ukraine but gave contradictory reasons for the decision.
- Call Memorandum: On September 25, 2019, the Trump administration released the official transcript (or memorandum) of the phone call between Trump and Zelenskyy, which confirmed the requests to investigate Biden and Hunter Biden. Trump asked Zelenskyy to work with Giuliani and U.S. Attorney General William Barr on the investigation.
- Testimonies from Officials: Multiple witnesses, including key diplomats and members of Trump’s administration, confirmed that the request was made not in line with official foreign policy objectives but as part of Trump’s political campaign.
Abuse of Power and Obstruction of Congress
On December 13, 2019, the House Judiciary Committee, which oversaw the impeachment inquiry, passed two articles of impeachment:
- Abuse of Power – Trump was accused of using his office to solicit foreign interference in the 2020 election.
- Obstruction of Congress – Trump was charged with blocking the House’s impeachment inquiry by instructing officials not to comply with subpoenas for documents and testimonies.
The full House of Representatives impeached Trump on both counts on December 18, 2019.
Impeachment Trial in the Senate
The trial started in January 2020, where House impeachment managers asserted that Trump’s actions represented the type of corruption the Founding Fathers aimed to address through impeachment. Trump’s legal team denied the facts of the charges, arguing that abuse of power was not a crime and that he was not charged with an actual criminal act.
- No Witnesses: The trial was unprecedented as it was the first in U.S. history to proceed without witness testimony. The Senate, with a Republican majority, voted to not subpoena witnesses or documents, significantly limiting the trial’s scope.
- Final Vote: On February 5, 2020, the Senate acquitted Trump of both charges. Senator Mitt Romney was the only Republican to vote for conviction, citing Trump’s abuse of power as the reason, but ultimately joining the majority in acquitting him.
After the acquittal, Trump removed several officials from office who were perceived as disloyal or insufficiently supportive, further demonstrating the tense nature of his relations with those who spoke out against his actions.
Second Impeachment: Incitement of Insurrection
Capitol Riot & Impeachment Charge
After losing the 2020 presidential election to Joe Biden, Trump continuously spread unfounded claims of election fraud. This culminated in the January 6, 2021 Capitol riots, when a mob of Trump supporters stormed the U.S. Capitol in an attempt to block the certification of Biden’s victory. The violence led to deaths and injuries, shocking the nation.
On January 11, 2021, Speaker Pelosi introduced the second article of impeachment, charging Trump with incitement of insurrection. This charge came after Trump’s inflammatory rhetoric, where he encouraged his supporters to “peacefully and patriotically” march to the Capitol, while also implying other more aggressive actions.
House Impeachment Vote
On January 13, 2021, the House of Representatives voted 232–197 to impeach Trump. This made Trump the first U.S. president to be impeached twice. This time, ten Republicans joined Democrats in voting for impeachment—the largest number of members from the president’s own party to vote for impeachment in U.S. history.
- Argument Against Trump: The articles outlined how Trump’s rhetoric and actions leading up to January 6 helped incite an armed and violent attack on the U.S. government.
- Historical Context: With this vote, Trump’s second impeachment marked a key moment in U.S. history, a stark repudiation from a portion of his own party.
Senate Trial After Trump Leaves Office
Trump’s impeachment trial began in February 2021, after Trump had already left office. This was unprecedented, as it had never happened that a president was tried after leaving office. A heated debate centered around whether the Senate had the jurisdiction to try a former president.
- The Senate’s Constitutional Debate: The Senate ultimately voted 56–44 that the trial was constitutional. The result was 10 votes shy of the 67 needed to convict.
- Impeachment Trial Outcome: On February 13, 2021, after a five-day trial, the Senate acquitted Trump. However, this time, the vote saw seven Republican senators join all Democrats in voting to convict him. This marked the most bipartisan impeachment vote in U.S. history.
- Majority Vote: Despite the seven Republican votes, Trump was not convicted, and he was acquitted once again.
Implications of Acquittal
While Trump was acquitted, the Republican Party’s internal division was evident during this process, especially as many of the party’s senators were forced to decide whether to maintain loyalty to Trump or distance themselves after the violence at the Capitol. Despite his acquittal, Trump’s role in the January 6th events and his incitement continued to create a rift in U.S. politics and legal discourse.
Legacy of Both Impeachments
- First Impeachment: Trump’s first impeachment laid bare a deep division in U.S. politics over the boundaries of presidential power and foreign influence in elections. While the acquittal strengthened Trump’s base, it also galvanized critics who saw it as a disregard for democratic values.
- Second Impeachment: The second impeachment underscored the dangerous consequences of political rhetoric in inciting violence and a breakdown of constitutional order. Trump’s acquittal may have slowed political accountability, but it led to increasing calls for reforms to prevent future presidential misconduct.
January 6 Capitol attack
On January 6, 2021, a tragic and unprecedented event unfolded in American history when pro-Trump supporters stormed the U.S. Capitol as Congress was in the midst of certifying the results of the 2020 Presidential Election. The incident is often viewed as an attempted self-coup, orchestrated by Donald Trump’s inflammatory rhetoric, urging his supporters to challenge the electoral outcome. It stemmed from months of disinformation and unfounded allegations of election fraud, continuously peddled by Trump and his allies. Leading up to this fateful day, Trump made a series of controversial moves that alarmed high-ranking officials in the military and intelligence agencies.
In December 2020, there were growing concerns at the Pentagon about Trump’s actions and the possibility of a military coup or aggressive foreign action. With Mark Milley, Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff, and CIA Director Gina Haspel expressing worries, the tension heightened after Trump had moved supporters into influential military positions. These concerns became more pronounced as military leaders expressed uncertainty about Trump’s motives and potential actions. Milley emphasized that the military should have no involvement in the election or any political processes, particularly when it came to interfering in a democratic election or employing military force to influence the election results.
Despite these concerns, on January 6, 2021, Trump held a rally at the Ellipse near the White House, while the official Congressional certification of the election results was taking place. Trump’s speech became a pivotal moment in the timeline of events, where he falsely reiterated the claim that the 2020 election was stolen. He encouraged the assembled crowd of his supporters to “fight like hell” and urged them to take back the country, directly suggesting that they march to the U.S. Capitol to disrupt the certification of Joe Biden’s victory. This inflammatory rhetoric acted as a catalyst for the violent actions that followed.
As Trump finished his speech, thousands of his supporters began marching toward the Capitol. What followed was nothing short of chaos. The rioters clashed violently with law enforcement and breached the Capitol building itself, disrupting the proceedings of Congress and forcing the evacuation of lawmakers. They damaged property, vandalized offices, and left behind a trail of destruction. Within hours, the Capitol became a scene of violence and tension. The rioters were intent on halting the certification of Joe Biden’s election victory and were able to create havoc long enough to disrupt the Congress’s scheduled functions. The event caused extensive damage not only to the building but also to the security and public trust in American democracy.
Throughout the chaotic scenes, Trump remained noticeably absent from taking decisive action. Despite being aware of the situation unfolding at the Capitol, Trump posted several messages on Twitter that served to prolong the violence. His infamous tweet at 6 p.m. suggested that the rioters should “go home with love & in peace,” offering praise for them by calling them “great patriots.” However, he never issued an unequivocal message to denounce the attack or call for an immediate cessation of hostilities. Instead, he reiterated false claims about the election being rigged. His response, or lack thereof, was criticized heavily, with many believing his statements indirectly emboldened the rioters.
As night fell, Congress reconvened after the Capitol was secured, continuing its work and eventually certifying Joe Biden’s victory. By early the next morning, the official result was declared, though the nation had already been deeply shaken by the events that transpired. The rioting had resulted in the deaths of five people—including a Capitol police officer—and over 140 law enforcement injuries. The violent breach and desecration of the Capitol shocked the world, highlighting the volatility surrounding U.S. politics and the capacity for violent extremism in the modern era.
In the weeks following the attack, the damage continued, both in terms of physical destruction and the erosion of trust in democratic institutions. Legal and congressional investigations into the Capitol attack intensified. Trump’s actions during the riot, as well as his rhetoric leading up to the attack, were subjects of immense scrutiny. The backlash he faced led to a second impeachment in the House of Representatives, making him the first president in history to be impeached twice. Yet, despite bipartisan condemnation, Trump remained defiant, continuing to repeat baseless claims of election fraud, while many of his actions during the aftermath contributed to his enduring legacy of turmoil.
Beyond the impeachment, Trump’s relationship with the individuals involved in the riot further complicated his position. As the months wore on, Trump even aligned himself with some of the rioters who had been arrested and incarcerated. He collaborated with them on a song to raise money for their legal defenses. This was part of his broader approach in which he expressed support for many individuals charged in connection with the violence at the Capitol. In June 2023, Trump publicly declared that, if he were to be reelected, he would consider offering pardons to many of those who took part in the violent disruption.
The fallout from January 6 would have far-reaching effects on American politics, security protocols, and democracy as a whole. It triggered a series of legal consequences for both the perpetrators and those responsible for fueling the insurrection, leading to hundreds of convictions. It raised broader questions about democratic backsliding, the fragile nature of peaceful transitions of power, and the risks of divisive political rhetoric. The January 6 Capitol attack was not just an attack on a building, but on the fundamental principles of American governance itself, shaking the public’s confidence in its institutions and its future.
Between presidencies (2021–2025)
After leaving the White House in January 2021, Donald Trump returned to his Mar-a-Lago resort in Palm Beach, Florida, where he established an office, in line with provisions under the Former Presidents Act. In the months following his departure from office, Trump continued to dominate the political landscape, especially within the Republican Party. His relentless false claims about the 2020 presidential election, commonly referred to by critics as “the big lie,” remained a prominent theme in his post-presidential rhetoric. Initially, Trump’s false accusations about election fraud were central to his discourse, but by May 2021,
he appropriated the term “the big lie” to refer to the election itself, reinforcing the narrative of its illegitimacy despite the lack of supporting evidence. These claims were not just a personal crusade for Trump; they became a rallying point for Republicans, many of whom used his rhetoric to justify passing new voter suppression laws designed to favor their party’s interests in future elections.
Unlike other former presidents, Trump maintained an unprecedented level of influence within his party. He was referred to by a 2022 New York Times profile as a modern party boss due to his continued control over Republican politics. Trump became highly involved in fundraising, building an impressive financial war chest—outpacing even the funds available to the Republican National Committee. He made a significant profit from fundraising events held at Mar-a-Lago, and continued shaping the Republican Party’s governance by installing key officials loyal to him. Trump’s political sway was evident during the 2022 midterm elections, where he endorsed over 200 candidates for various offices, exerting a considerable influence over local and national elections.
In addition to his political efforts, Trump returned to business ventures. In February 2021, he registered a new company, the Trump Media & Technology Group (TMTG), with the goal of providing social media services to U.S. customers. The company moved to become a publicly traded entity in March 2024, following a merger with the special-purpose acquisition company (SPAC) Digital World Acquisition. TMTG launched the Truth Social platform in February 2022, aimed at offering an alternative to more mainstream social media platforms such as Twitter and Facebook—which had censored Trump’s posts due to violations of their policies.
Despite his continued influence and business ventures, Trump’s post-presidential years were marred by ongoing legal challenges, which brought significant scrutiny to his actions while in office and afterwards. He is now the only U.S. former president to be convicted of a crime, a record that highlights the legal repercussions of his actions.
The most significant legal investigations that Trump faced stemmed from his handling of government documents. Upon leaving the White House, it was revealed that Trump had taken classified White House documents to Mar-a-Lago. In May 2021, the National Archives and Records Administration (NARA) discovered that several important documents had not been handed over as required. They requested that Trump’s office retrieve these materials. By January 2022, 15 boxes of these materials—some containing classified information—were returned.
Later that year, the Justice Department initiated an investigation into Trump’s handling of the documents and subpoenaed his office for additional materials. Despite Trump’s lawyers claiming in a statement that all classified material had been returned, the FBI executed a search warrant at Mar-a-Lago on August 8, 2022, to seize additional materials related to potential violations of the Presidential Records Act, which governs the handling of government records. Reports suggested that some of these documents were highly classified, even touching on sensitive matters such as nuclear weapons.
This FBI search raised concerns regarding violations of the Espionage Act and laws related to obstruction of justice, particularly since the search yielded over 11 sets of classified documents, including four marked as “top secret,” and one as “top secret/SCI,” the highest level of classification in the United States government. The growing legal scrutiny led to the appointment of Jack Smith, a federal prosecutor, as a special counsel to oversee investigations into both the Mar-a-Lago document case and Trump’s role in the January 6 Capitol attack. As the situation developed, Trump’s legal woes deepened, setting the stage for a complex legal battle over his actions both as president and as a private citizen post-presidency.
Criminal referral by the House January 6 Committee
In the aftermath of the January 6 Capitol attack, legal proceedings against Donald Trump intensified. On December 19, 2022, the United States House Select Committee on the January 6 Attack made a significant move by recommending criminal charges against the former president. These charges included obstructing an official proceeding, conspiracy to defraud the United States, and inciting or assisting an insurrection. The recommendation was part of the committee’s ongoing investigation into Trump’s role in the Capitol insurrection, focusing on whether his actions and statements leading up to the event violated U.S. law.
Simultaneously, Trump faced criminal consequences from both state-level charges and federal investigations, further adding to the legal complications surrounding his post-presidential years.
In December 2022, the Trump Organization was convicted of 17 counts of criminal tax fraud, conspiracy, and falsifying business records. This conviction came after a lengthy investigation and jury trial, though Trump himself was not personally charged. Following the conviction, the organization was fined the maximum amount of $1.6 million, and its Chief Financial Officer, Allen Weisselberg, was sentenced to jail. These developments marked a critical moment for Trump’s business empire, though it did not result in charges directly against him.
In January 2023, the legal fallout from Georgia’s 2020 election continued, with a Fulton County grand jury indicting Trump on 13 charges, including racketeering, for allegedly attempting to manipulate the election outcome. The charges stemmed from his phone call to Georgia officials, urging them to “find” the votes needed to overturn the election results. Trump surrendered, was processed at the Fulton County Jail, and released on bail. However, he pleaded not guilty to the charges, and in March 2024, a judge dismissed three of the 13 charges, demonstrating a shift in some of the legal proceedings against him.
On the federal level, Trump’s legal troubles deepened. In June 2023, following a special counsel investigation, a Miami federal grand jury indicted Trump on 31 counts related to his willful retention of national defense information under the Espionage Act, and additional charges of making false statements, conspiracy to obstruct justice, and withholding and concealing documents. These charges were related to his possession of classified documents that had not been returned to the National Archives following his exit from the White House. Trump pleaded not guilty to these charges, and a superseding indictment added further charges the following month.
Legal disputes also extended to the handling of the trial itself. Trump’s appointed judge, Aileen Cannon, had previously made rulings in his favor, but her decisions in this case faced challenges. In May 2024, she postponed the trial indefinitely and later ruled that the appointment of the special counsel was unconstitutional. However, the special counsel, Jack Smith, appealed the dismissal, highlighting the continued legal complexities.
Trump’s legal troubles intensified once again in August 2023 when another federal grand jury indicted him for his attempts to overturn the 2020 election results. The charges focused on his role in conspiring to defraud the U.S., obstructing the certification of the Electoral College vote, and trying to deprive voters of their rights by preventing their votes from being counted. Trump, again, pleaded not guilty to these charges. However, in November 2023, a judge dismissed this specific case after the prosecution cited a Department of Justice policy in its motion to dismiss. This ruling was seen as a temporary setback, with the appellate court continuing to weigh in on other cases concerning Trump.
In January 2025, the Justice Department released a detailed report from the special counsel, which accused Trump of engaging in an “unprecedented criminal effort” to overturn the results of the 2020 election. The ongoing investigations and legal challenges suggest that Trump’s post-presidency years could be defined by continuous litigation, which continues to dominate discussions around his legal legacy.
Criminal conviction in the 2016 campaign fraud case
In relation to his 2016 presidential campaign, Donald Trump found himself embroiled in significant legal issues due to payments made to two women, Stormy Daniels and Karen McDougal, who allegedly had affairs with him in 2006 and 2007. Both women were reportedly paid for their silence about these affairs during the election campaign, with American Media, Inc. (AMI), publisher of the National Enquirer, and a company organized by Trump’s lawyer Michael Cohen, allegedly behind the payments. Cohen, in 2018, pleaded guilty to violating campaign finance laws, admitting that he had arranged the payments at Trump’s direction with the intention of influencing the election by keeping the alleged affairs secret.
Although Trump denied having affairs with Daniels and McDougal and initially claimed no knowledge of the payments made to Daniels, he reimbursed Cohen in 2017 for the money paid to her. The FBI investigated the matter, especially after Trump was linked to phone calls with Cohen in October 2016, indicating his direct involvement in the arrangement. The FBI closed its investigation into the payments in 2019, but two years later, both the New York State Attorney General’s Office and the Manhattan District Attorney’s Office launched criminal investigations into Trump’s financial dealings, focusing on his business activities, including the hush money scheme.
In March 2023, the New York grand jury indicted Trump on 34 felony charges related to falsifying business records to classify the hush money payments as legitimate business expenses, thus attempting to sway the outcome of the 2016 election. By May 2023, Trump was convicted on all charges. Despite this conviction, on January 10, 2025, he was sentenced to unconditional discharge, which meant the conviction was upheld, but without any additional punitive measures under New York law.
In addition to these criminal charges, Trump was also mired in a series of civil lawsuits and judgments that stemmed from his business practices and personal conduct. In September 2022, the New York Attorney General filed a civil fraud lawsuit against Trump, his three eldest children, and his business, the Trump Organization, accusing them of inflating asset values to secure favorable loans and lower insurance premiums.
In August 2022, during a deposition for the case, Trump invoked the Fifth Amendment more than 400 times to avoid self-incrimination. After months of legal proceedings, a New York judge ruled in September 2023 that Trump and his company had committed fraud. The court ordered the dissolution of the Trump Organization’s business entities and the cancellation of its New York business certificates.
In February 2024, Trump was found liable for fraud and was ordered to pay over $450 million in penalties and interest. This ruling also barred him from holding any leadership positions in New York-based companies for three years. He contested these judgments, intending to appeal. Meanwhile, an independent monitor was appointed to oversee the operations of the business, ensuring compliance with the court’s rulings and guiding the company through possible restructuring.
The legal ramifications continued to mount with civil lawsuits alleging defamation and misconduct. In May 2023, Trump faced a significant legal loss in a federal lawsuit filed by journalist E. Jean Carroll, who accused him of sexual abuse and defamation. The jury found him liable and ordered him to pay $5 million. Although Trump sought a new trial and appealed the decision, the court upheld the ruling, determining that Carroll’s allegations were “substantially true.”
The defamation saga between Trump and Carroll extended further when, in January 2024, another jury awarded $83.3 million in damages in Carroll’s earlier defamation case (“Carroll I”), ruling that Trump had falsely branded her allegations as lies. Although Trump continued to pursue appeals in both the sexual abuse case (“Carroll II”) and the defamation case, he was confronted by further legal troubles.
As of December 2024, Trump’s legal entanglements were far from resolved. He faced a collection of ongoing civil lawsuits related to various allegations, including his actions surrounding January 6, his role in clearing racial justice protesters from Lafayette Square, and a defamation case from members of the Central Park Five. The sheer volume and gravity of these cases indicated that Trump’s legal woes were likely to continue dominating public and political discourse for the foreseeable future.
2024 presidential election
n the 2024 presidential election, Donald Trump made a dramatic return to the political stage. Announcing his candidacy on November 15, 2022, he quickly established a fundraising apparatus to support his campaign, with part of the donations being diverted to his leadership PAC. By March 2024, his campaign had already directed a significant portion of its funds towards covering his extensive legal bills, totaling $100 million.
However, Trump’s campaign encountered legal challenges. In December 2023, the Colorado Supreme Court ruled that he was disqualified from appearing on the ballot for the Colorado Republican primary due to his involvement in inciting the January 6, 2021 Capitol riot. Nevertheless, in March 2024, the U.S. Supreme Court ruled in his favor, restoring his eligibility to run, with a unanimous decision stating that Colorado did not have the authority to enforce Section 3 of the 14th Amendment, which bars insurrectionists from holding federal office.
As the campaign progressed, Trump escalated his rhetoric, making violent and authoritarian statements. He notably stated that, if elected, he would use the FBI and Justice Department against political opponents and intended to mobilize the military to target Democratic politicians and critics of his candidacy. His inflammatory anti-immigrant speech became more pronounced compared to his previous campaigns, and he adopted a fascist, authoritarian style of rhetoric. These statements sparked widespread concern among both political commentators and historians who described his rhetoric as extreme and unprecedented in American politics.
A growing sense of unease surrounded Trump’s health as he appeared increasingly unfit for office, with experts noting his rambling speech and behavioral disinhibition, raising questions about his ability to serve another term. His campaign was also marred by his frequent claims of a rigged election and election interference, echoing his accusations from 2020, but amplified with even more intensity. Trump’s unwillingness to commit to accepting the 2024 election results was seen as a continuation of his earlier refusal, reinforcing his narrative of “heads I win, tails you cheated.”
Tragedy struck in July 2024 when an assassination attempt was made on Trump during a campaign rally in Butler Township, Pennsylvania, where a bullet grazed his ear. The tension escalated further with another assassination attempt on September 15, 2024, in Florida. Despite these challenges, Trump remained steadfast in his bid for the presidency.
By November 2024, Trump triumphed in the presidential election with 312 electoral votes, defeating incumbent Vice President Kamala Harris, who secured only 226 electoral votes. Trump’s victory marked his second, nonconsecutive term as President, making him only the second U.S. president in history to achieve such a feat (after Grover Cleveland in 1892). Trump also won the popular vote, receiving 49.8% of the vote to Harris’s 48.3%, with a margin narrower than any since the 2000 election.
Trump’s victory was especially remarkable because it indicated his growing support among key demographics. He notably gained ground among working-class voters, especially young men, voters without college degrees, and Hispanic voters, improving his performance compared to the 2020 election. The media, including outlets like The Associated Press and BBC News, hailed Trump’s win as a remarkable comeback, recognizing it as part of a broader global trend of backlash against incumbent parties, especially amid the economic strain of the 2021–2023 inflation surge.
Political practice and rhetoric
Donald Trump’s second presidency, which began on January 20, 2025, saw him make history as the oldest individual to assume the office of the president and the first to enter his second term while having a felony conviction. With his swearing-in ceremony at the Capitol, Trump’s presidency ushered in a host of early actions that sought to steer the country back toward his previous policies, while further reinforcing his divisive stance on various domestic and international issues.
Upon taking office, Trump wasted no time in implementing significant executive orders aimed at dismantling certain legacies of the previous administration, as well as realigning U.S. priorities. One of his first moves was the withdrawal of the United States from two major international agreements: the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Paris Climate Agreement. Both of these actions were deeply reflective of Trump’s ongoing skepticism toward multilateral organizations, which he had previously criticized for their perceived limitations on American sovereignty and economic growth. His administration had previously pulled the U.S. out of the Paris Agreement during his first term, and his reaffirmation of this stance underscored his preference for deregulation over international collaboration in combating climate change.
In his inaugural executive actions, Trump also took steps to reshape how the U.S. government operates on a domestic level. He began by rolling back the recognition of genders outside of male and female, signaling his administration’s strict approach toward definitions of identity. These moves were viewed by many as an effort to solidify traditional conservative values, especially amid ongoing debates regarding the rights of gender non-conforming individuals. He took further action by freezing new regulations and pausing the hiring of federal workers, aiming to reduce the size and scope of the federal government, a hallmark of his policies from the previous term.
One of the defining actions of Trump’s early days in office was the establishment of the Department of Government Efficiency, a new entity that aimed to streamline government functions and reduce waste. In parallel, his administration barred the federal government from becoming involved in criminal investigations of political adversaries, marking a shift in how U.S. law enforcement interacted with political figures, particularly those from opposing parties. Trump’s controversial style extended to free speech, as his administration took steps to prevent government censorship, aligning with his vocal criticisms of what he perceived as mainstream media bias and the suppression of conservative viewpoints.
Trump’s stance on foreign policy and national security was another critical area where his second term mirrored the aggressive approaches of his first presidency. He acted swiftly to reverse multiple foreign and domestic policies. A key example of this was the decision to roll back sanctions on Israeli settlers, thereby aligning with pro-Israel factions within the United States. Additionally, his administration sought to further isolate Cuba, a country that had previously experienced a thaw in relations with the U.S. under President Barack Obama’s administration.
Trump’s political maneuvers also reflected his broader vision to consolidate power among his loyal supporters, which included implementing actions like granting a mass pardon to approximately 1,500 rioters involved in the January 6 Capitol attack. This move seemed to be a calculated gesture aimed at reinforcing his base, particularly those in favor of a more punitive approach to law enforcement for political reasons.
The border crisis remained a top issue during Trump’s second presidency. One of his most notable policies included the national emergency declaration for the southern border, which aimed to prompt the deployment of armed forces to counter illegal immigration. This was framed as part of his “America First” agenda, which focused on ensuring that the needs and safety of U.S. citizens took precedence over broader humanitarian concerns.
Domestically, Trump’s economic policy continued to favor tax cuts, deregulation, and stringent immigration reform. As part of his ongoing trade battles, on January 21, 2025, he made headlines by threatening to impose a 25% tariff on imports from both Canada and Mexico, warning that it would take effect by February 1, 2025. While it was unclear whether this threat would materialize, it demonstrated Trump’s focus on reshaping global trade terms in favor of the U.S. economy, potentially leading to retaliatory actions from these neighboring nations.
On the international stage, Trump’s second administration placed a heavy emphasis on shaping relationships with countries that had been contentious during his first term. In January 2025, his administration helped broker a ceasefire between Israel and Hamas alongside the outgoing Biden administration, signaling a potential shift in Middle Eastern diplomatic dynamics under his leadership. This partnership in international diplomacy was seen as an attempt to pave the way for a smoother transition while also reaffirming his aggressive diplomatic stance when dealing with foreign adversaries.
Despite a flurry of executive orders and foreign policy changes, Trump’s second term is marked by deep divisions both within the country and in the international arena. His stance on numerous social issues, such as immigration, gender identity, and global cooperation, continued to spark national debates about the future direction of U.S. governance. Many critics highlighted that his approach to both domestic policy and foreign relations risked deepening fractures in American society, further polarizing voters, while some supporters viewed these same actions as a strong reaffirmation of conservative principles that had previously found success in his first term.
Overall, Trump’s second presidency has the potential to shape U.S. policies for years to come, with his bold executive actions reaffirming his continued commitment to reshaping the federal landscape while addressing the needs of his political base. The presidency of Donald Trump in 2025 sets the stage for further political, legal, and international challenges as the U.S. grapples with the complex questions of governance in a rapidly changing world.
Link to violence and hate crimes
Donald Trump’s tenure as president has been closely linked to an increased level of political violence and hate crimes, with critics attributing much of this escalation to his rhetoric and actions. One of the most notable instances that intensified these concerns occurred during a 2020 presidential debate when Trump refused to condemn the white supremacist group Proud Boys. His statement, “Proud Boys, stand back and stand by,” was widely interpreted as an endorsement, contributing to the group’s recruitment and the emboldening of far-right extremists. His rhetoric often appeared to normalize white nationalism and encouraged violence among his supporters, with many of the individuals involved in politically motivated crimes citing his statements as justification for their actions.
Trump’s influence has been deemed pivotal in fostering political extremism, as he has frequently embraced or tolerated conspiracy theories and far-right militias. His repeated support for extreme positions and disregard for conventional political norms has been linked to an uptick in political violence, which spans both threats and actual violent events. Stochastic terrorism, a term describing the use of rhetoric that indirectly incites violence, has been used to describe Trump’s approach to politics. By inflaming passions and elevating fears about various groups, including immigrants and political adversaries, his language and actions have stirred violence in real-world settings, a trend not seen to the same degree in previous American presidencies.
Research and studies highlight the association between Trump’s discourse and a rise in hate crimes, particularly those targeting racial and ethnic minorities. Following his ascendancy to power, communities of color became increasingly vulnerable to attacks, with right-wing extremists becoming more emboldened. Many violent actors from the storming of the U.S. Capitol in 2021 and other incidents cited Trump’s influence on their ideologies and actions, suggesting that his rhetoric contributed to a culture in which hate crimes were seen as acceptable or even encouraged. For instance, a report by ABC News in 2020 identified at least 54 criminal cases linked to Trump’s rhetoric, mostly perpetuated by white men who targeted minorities.
In the domain of conspiracy theories, Trump’s engagement with and promotion of numerous unfounded claims has been another hallmark of his presidency. The former president became synonymous with propagating conspiracy theories, some of which had serious implications for public trust in institutions and democratic processes. One of the earliest and most significant conspiracy theories promoted by Trump was birtherism, in which he claimed that President Barack Obama was not born in the U.S., despite the fact that Obama’s birthplace had been well-documented. In addition to this, Trump endorsed a range of fringe theories, including the QAnon movement, which claimed that a deep state of elites-controlled world events and that Trump was a savior sent to defeat them.
Trump’s willingness to spread these conspiracy theories extended beyond mere rhetoric, with many of these theories influencing his administration’s policies and strategies. He backed the Clinton body count theory, propagated rumors about global warming being a hoax, and supported unsubstantiated claims about election fraud during his 2020 presidential defeat. His “Big Lie”—the claim that the 2020 election was stolen from him—was central to his efforts to overturn the election results and inspired the January 6th Capitol insurrection, further exemplifying his role in undermining democratic processes.
The prevalence of falsehoods and misleading statements made by Trump, especially during his campaign and presidency, has been a consistent feature of his public life. Fact-checking organizations such as The Washington Post have tallied over 30,000 false or misleading statements during his time in office, reflecting an unprecedented volume of misinformation from a sitting president. Some of Trump’s most contentious falsehoods had tangible impacts on public health and safety. For example, his promotion of hydroxychloroquine as an effective treatment for COVID-19 led to shortages and panic-buying, despite limited scientific backing for the drug’s effectiveness.
Furthermore, Trump’s stance on mail-in voting and election integrity undermined confidence in the American electoral system. His repeated attacks on the legitimacy of elections fueled conspiracy theories and doubts about the political process, culminating in the January 6th Capitol riot, a violent and historic event meant to disrupt the certification of Joe Biden’s victory.
Trump’s disregard for truth and his failure to apologize for spreading misinformation have been consistently noted as key elements of his political identity. His behavior did not only weaken trust in public institutions, but it also worsened an already polarized national atmosphere, exacerbating existing divides among the American populace. Despite overwhelming evidence proving the falsehood of many of his statements, Trump maintained his position and continued to promote disinformation, largely unhindered by any significant political or legal repercussions.
In conclusion, Donald Trump’s rhetoric, actions, and widespread propagation of misinformation have had a profound impact on American society, fueling political violence, hate crimes, and a growing culture of distrust toward institutions and the democratic process itself. His approach has reshaped American political discourse, influencing both supporters and detractors, leaving a lasting imprint on the country’s political landscape.
Social media
Donald Trump’s relationship with social media was pivotal during his presidency, both for his direct communication with the public and the controversies surrounding the spread of misinformation. Trump’s presence on social media, particularly Twitter, played a central role in his rise to political power, especially during his 2016 presidential campaign. He often used Twitter to bypass traditional media channels, allowing him to directly address his followers and express his views. His use of social media became a hallmark of his political style, where his tweets were treated as official statements by the White House at one point, even leading to friction with established press outlets that were increasingly sidelined.
Throughout his presidency, Trump’s tweets were subject to widespread scrutiny. His frequent and often unfiltered remarks on Twitter allowed him to communicate directly with his base, but they also led to a constant flow of misinformation. The platform took steps in 2020 to tag some of his tweets with fact-check warnings, responding to criticisms for allowing the spread of falsehoods. In May 2020, Trump responded by attacking social media platforms, accusing them of silencing conservative voices and calling for strong regulation or the closure of such companies. This tense relationship escalated following the January 6 Capitol attack in 2021, which led to a permanent ban from Twitter, Facebook, and Instagram, drastically limiting his ability to influence the national narrative.
After the loss of his social media accounts, Trump launched his own platform, Truth Social, in early 2022. However, this platform attracted a significantly smaller following compared to his Twitter audience, further showing the challenges of building an online presence independent of mainstream social networks. In 2022, after Elon Musk acquired Twitter, Trump’s Twitter account was reinstated, although his presence remained limited compared to his previous social media dominance.
Trump’s relationship with the press has also been marked by antagonism and conflict, creating a “love-hate” dynamic that persisted throughout his career. His media strategy relied heavily on maintaining a combative stance against reporters and outlets he deemed biased, frequently referring to the media as “fake news” and “the enemy of the people”. He skillfully exploited his confrontations with the press, turning them into narratives that helped reinforce his image as a political outsider, fighting against a supposedly hostile establishment. His relationship with journalists was a key aspect of his communication strategy, where discrediting media outlets allowed him to control his narrative.
During his presidency, Trump increasingly reduced formal press briefings, holding far fewer than his predecessors, and cut down on media access to the White House. He also employed legal tactics to challenge and silence journalists who reported unfavorably on him. Notable legal actions include defamation lawsuits filed against major outlets like The New York Times, The Washington Post, and CNN, although these suits were largely dismissed. Trump’s disdain for the media also extended to calls for more drastic measures, including prosecuting media companies and threatening to revoke broadcast licenses for spreading what he considered “bad stories” about him.
In 2024, he continued to attack the media, even suing ABC News for defamation after a report on his civil lawsuit for alleged rape. The case was settled with a donation from the network’s parent company, Walt Disney, to his future presidential library. Trump’s continuing confrontations with the media and his attempts to control the narrative around him remain a defining aspect of his public persona, blurring the lines between truth, rhetoric, and power in the modern media landscape.
Personal Life
Family
In 1977, Trump married Czech model Ivana Zelníčková. They had three children: Donald Jr. (b. 1977), Ivanka (b. 1981), and Eric (b. 1984). Their marriage ended in 1990 following Trump’s affair with model and actress Marla Maples. Trump married Maples in 1993, but they divorced in 1999. They have one daughter, Tiffany (b. 1993), whom Maples raised in California. In 2005, Trump married Slovenian model Melania Knauss, and they have one son, Barron (b. 2006).
Health
Trump has claimed that he has never drunk alcohol, smoked cigarettes, or used drugs. He reports sleeping about four or five hours a night. Trump has stated that golfing is his primary form of exercise, though he typically does not walk the course. He believes that exercise is a waste of energy, describing the body as “like a battery, with a finite amount of energy,” which is depleted by physical activity.
In 2015, his campaign released a letter from his long-time physician, Harold Bornstein, stating that Trump would be “the healthiest individual ever elected to the presidency”. However, in 2018, Bornstein revealed that Trump had dictated the contents of the letter, and three of his agents had seized his medical records during a raid on Bornstein’s office in February 2017.
Religion
Trump identified as a Presbyterian and a Protestant in 2016, but by 2020, he began to describe himself as a nondenominational Christian. He attends church on Sundays and has stated that he maintains strong relationships with Christian ministers. In 2024, Trump started selling special editions of the King James Version of the Bible, which included copies of the founding documents of the United States, marketed as the God Bless the U.S.A. Bible. Trump is also known to have a personal collection of Bibles.
Assessments
Public Image
A Gallup poll conducted across 134 countries between 2016 and 2017 found that Trump had a higher job approval rating than Obama in 29 countries, mostly non-democracies. However, the approval of U.S. leadership plummeted among allies and G7 countries. By mid-2020, only 16 percent of international respondents from a 13-nation Pew Research poll expressed confidence in Trump, which was lower than the approval ratings for Xi Jinping of China and Vladimir Putin of Russia.
During his first presidency, research in 2020 found that Trump had a stronger impact on public assessments of American political parties and partisan opinions than any other president since Harry Truman. In 2021, Trump was the only president never to reach a 50 percent approval rating in Gallup polling, which had been conducted since 1938.
This was partially due to a record-high partisan gap in his approval ratings, with 88 percent approval from Republicans compared to just 7 percent from Democrats. Trump’s approval ratings remained unusually stable, fluctuating between 35 percent and 49 percent, and he finished his term with a rating between 29 percent and 34 percent—the lowest of any president since modern polling began. His average approval rating throughout his presidency was 41 percent, which was also a record low.
Trump placed second to Obama in Gallup’s annual poll asking Americans to name the man they admire the most in 2017 and 2018, tied for first place in 2019, and placed first in 2020. He was the first elected president since Gallup started conducting this poll in 1946 not to be named most admired in his first year in office.
Scholarly Rankings
In the C-SPAN “Presidential Historians Survey 2021”, historians ranked Trump as the fourth-worst president in U.S. history. He received particularly low marks for his leadership characteristics, such as moral authority and administrative skills. In the Siena College Research Institute’s 2022 survey, Trump was ranked 43rd out of 45 presidents, with low ratings in nearly all categories except for luck, willingness to take risks, and party leadership. He ranked last in several areas. Furthermore, in both 2018 and 2024, surveys of members of the American Political Science Association ranked him as the worst president.