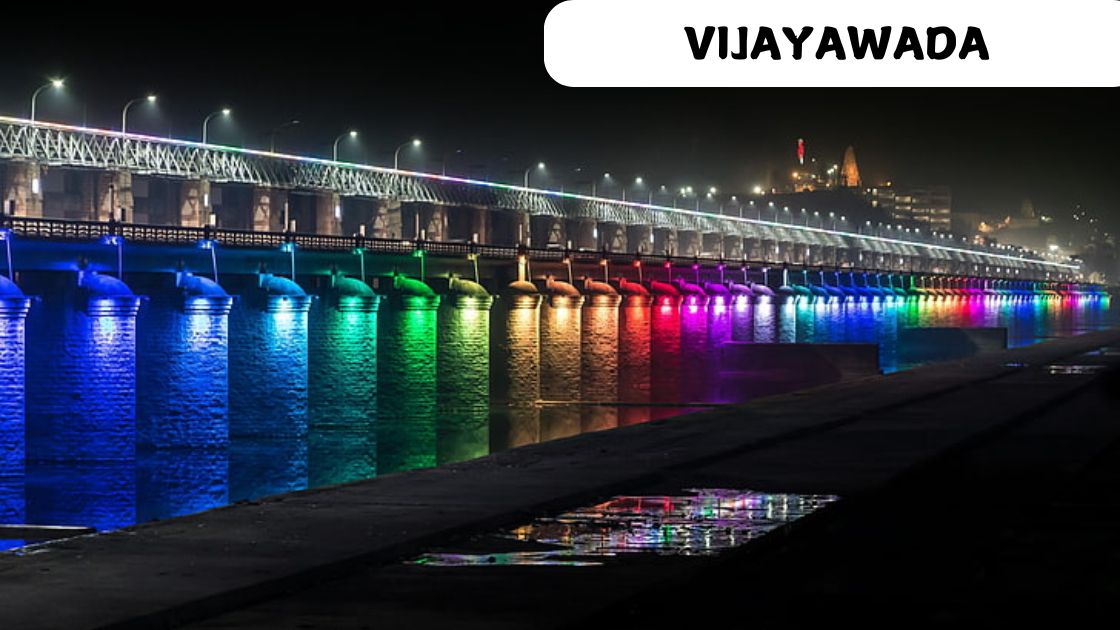
All about Vijayawada
Vijayawada, formerly known as Bezawada, is the second-largest city and a major commercial hub of Andhra Pradesh, strategically located at the center of the state. It sits along the banks of the Krishna River, surrounded by the Indrakeeladri Hills, which are home to the renowned Kanaka Durga Temple, a sacred Hindu site attracting countless devotees.
Recognized for its rapid urban growth, Vijayawada ranks among the world’s fastest-growing cities, as highlighted by an Oxford Economics report. As a part of the Andhra Pradesh Capital Region, it serves as the administrative headquarters of NTR district and boasts the Prakasam Barrage, which links the NTR and Guntur districts, showcasing its infrastructural significance.
Legend has it that Vijayawada, meaning “Land of Victory,” derives its name from mythological events. The city is associated with Goddess Durga’s victory over the demon Mahishasura and her repose on the Indrakeeladri Hill. The Mahabharata also links this place to Arjuna, who obtained the divine Pashupatastra from Lord Shiva here, reinforcing the city’s spiritual essence.
Vijayawada: A Thriving Hub of Spiritual Significance
Apart from being a sacred destination, Vijayawada is a vital economic and educational hub, attracting students from across the nation due to its premier institutions. As per McKinsey Quarterly, the city is projected to achieve a GDP of $17 billion by 2025, further solidifying its status as a “Global City of the Future.” Renowned for its dense urban population, it is ranked the third most densely populated urban area worldwide and among the top cities in India for livability, entertainment, construction, and healthcare.
Vijayawada’s rich history, modern significance, and strategic location have earned it national and international acclaim. It is connected through one of the busiest railway junctions in India, and its infrastructure positions it as a critical part of the state’s development roadmap. From its spiritual allure to its thriving economy, Vijayawada continues to shape Andhra Pradesh’s cultural, economic, and urban landscape.
History of Vijayawada
Vijayawada, historically known as Bezawada, has a rich history dating back to 626 A.D., when it was founded by the Paricchedi Kings. Over centuries, the city has evolved as a significant center for politics, culture, and religion in South India, making it a historically important site.
The Vishnukundina Era
The city’s early history is deeply tied to the Vishnukundina dynasty, which ruled the region during the 5th and 6th centuries. Under the reign of King Madhava Varma, Bezawada rose as a prominent town. The area also played a crucial role in the spread of Buddhism, attracting scholars like Xuanzang. The renowned Chinese Buddhist scholar stayed in Bezawada around 640 A.D. to study and transcribe the Abhidhamma Pitaka, part of the Theravada Buddhist scriptures. His accounts provide insights into the importance of the region as a center for learning.
Cultural and Religious Heritage
The Mogalrajapuram Hills stand as a testament to the city’s ancient architectural legacy, featuring five rock-cut temples believed to have been built between the 4th and 9th centuries. Some of these caves are attributed to the Vishnukundina dynasty. Another iconic site is the Akkana Madanna Caves, located at the base of the Indrakeeladri Hill, which is now recognized as a national monument.

At the foot of the same hill is the Malleswara Temple, which holds great historical and religious significance. The inscriptions at the temple date back to the 9th to 16th centuries, spanning various dynasties. Among the notable inscriptions are those issued by Yudhamalla I and II of the Eastern Chalukyas. These artifacts offer glimpses into the religious and cultural developments of that period.

Diamond Discoveries and the Qutb Shahi Dynasty
In the 16th century, during the reign of the Qutb Shahi dynasty (Golconda Sultanate), Vijayawada gained prominence due to the discovery of diamond mines near the banks of the Krishna River. These mines contributed to the wealth and reputation of the region, attracting traders and settlers from across India and beyond.

Monuments of Historical Importance
- Rock-Cut Temples at Mogalrajapuram Hills
These ancient temples are significant for their historical artistry and architectural prowess. - Akkana Madanna Caves
A symbol of South Indian rock-cut architecture, these caves date back to early centuries and are an attraction for historians and tourists. - Malleswara Temple
This temple reflects the religious history of Vijayawada, featuring inscriptions and relics from multiple dynasties.

Geography of Vijayawada
Located on the scenic banks of the Krishna River, Vijayawada is a city surrounded by hills, canals, and lush landscapes. At an elevation of 11 meters (36 feet) above sea level, it offers a picturesque natural environment shaped by its rivers, canals, and reservoirs.
Rivers and Canals
The city owes much of its geography and infrastructure to the Krishna River, which flows adjacent to it. From the Prakasam Barrage, three significant canals — Eluru, Bandar, and Ryves — originate and traverse through Vijayawada. These canals not only enhance irrigation facilities in the region but also lend an aesthetic appeal to the city.
Strategic Location and Connectivity
Vijayawada’s central location makes it a vital transport and commerce hub. The city’s placement along the river and its proximity to other regions of Andhra Pradesh make it pivotal in regional connectivity.
Climate of Vijayawada
Vijayawada features a tropical wet and dry climate (Köppen Aw), characterized by high temperatures and marked monsoonal influences.
Temperature Range
- The mean annual temperature ranges between 23.4–34°C (74–93°F), making the climate generally warm.
- Summers (April-May) are particularly hot, with May being the hottest month. The city’s highest recorded temperature was an astonishing 48.8°C (119.8°F) in May 2002.
- Winters (December-January) bring cooler temperatures, with the lowest ever recorded at 11.1°C (52°F).
Rainfall Patterns
Vijayawada receives rainfall from both the Southwest and Northeast monsoons. The annual average rainfall is 977.9 mm (38.50 inches), contributing to agriculture and water availability in the region.
| Rainfall Summary | Details |
|---|---|
| Wettest Months | July to October |
| Driest Months | January and February |
| Rainy Days per Year | ~54 days |
Humidity and Air Quality
Humidity averages at 60%, peaking during the monsoon months. Vijayawada also prioritizes sustainability, securing the 6th position in India’s ranking of “National Clean Air Cities” in the category of cities with over 10 lakh population.
Environmental Significance
The geographical elements, including rivers, hills, and favorable climate, have played an essential role in shaping Vijayawada’s identity as one of Andhra Pradesh’s major cities. Recognized for both natural beauty and sustainable living efforts, Vijayawada is poised to become an exemplary model for environmentally friendly urban development.
Demographics of Vijayawada
Vijayawada is the second most populous city in Andhra Pradesh and stands out globally as the third most densely populated urban built-up area, with approximately 31,200 people per square kilometer.
Population Statistics (2011 Census)
- Total Population: 1,021,806
- Males: 524,918
- Females: 523,322
- Sex Ratio: 997 females per 1000 males (higher than the national average of 940).
- Child Population (0–6 years):
- Total: 92,848
- Boys: 47,582, Girls: 45,266
- Child Sex Ratio: 951 girls per 1000 boys.
- Literacy Rate:
- Average: 82.59% (significantly above the national average of 73%).
- Male Literacy: 86.25%, Female Literacy: 78.94%.
- Total Literates: 789,038.
Language and Religion
Predominant Languages
- Telugu: The majority language, spoken by 89.42% of residents.
- Urdu: Spoken by 7.95% of the population, mainly among the Muslim community.
- Others: 2.63%, including Hindi, Tamil, Odia, Gujarati, Marathi, and Malayalam.
Religious Composition
Vijayawada showcases its cultural diversity through its religious demographics:
| Religion | Percentage | Population |
|---|---|---|
| Hinduism | 85.16% | 973,612 |
| Islam | 9.12% | 104,206 |
| Christianity | 3.64% | 41,557 |
| Jainism | 0.50% | 5,722 |
| Others/Unstated | 1.58% | 18,135 |
Highlights of Diversity
- Cultural Harmony: The city thrives on communal harmony, with a predominance of Hindu culture and notable contributions from Muslim and Christian communities.
- Linguistic Influence: While Telugu dominates, Urdu’s prevalence signifies the city’s rich historical and cultural connections. Smaller linguistic groups enrich the city’s multicultural fabric.
- Gender Inclusivity: A near-equal sex ratio highlights an essential step towards gender balance, accompanied by a relatively high literacy rate for women.
Vijayawada exemplifies a growing and urbanized demographic structure, making it an important cultural and economic hub in Andhra Pradesh.
Governance of Vijayawada
Civic Administration
The Vijayawada Municipal Corporation (VMC) is the primary governing body responsible for civic administration. It was India’s first urban local body to receive ISO 9001 certification for its quality management system. Established on April 1, 1888, it transitioned to a selection-grade municipality in 1960 and was upgraded to a municipal corporation in 1981.
Key administrative figures include:
- Municipal Commissioner: Sri Dhyanachandra H.M. (IAS)
- Mayor: Rayana Bhagya Lakshmi
The VMC oversees an area of 230 square kilometers (89 square miles) divided into 64 wards. As per G.O. 104 (March 2017), Vijayawada and its surrounding areas were declared a metropolitan area, accommodating a population of approximately 1.8 million. The metropolitan jurisdiction includes not just Vijayawada but also several surrounding villages and urban growth areas such as Mangalagiri and Tadepalle.
The city is also home to the Andhra Pradesh Capital Region Development Authority (APCRDA), which facilitates urban planning and development.
Utility Services
The VMC is responsible for a variety of essential urban services:
- Water Supply: Managed via 59 reservoirs to ensure city-wide access.
- Sewerage and Drainage: Vijayawada’s underground drainage system, operational since 1967–68, is a highlight of its civic infrastructure.
- Solid Waste Management: Produces 550 tonnes of solid waste per day, with ongoing recycling and green initiatives.
- Environment Protection: Maintains parks such as Rajiv Gandhi Park, Raghavaiah Park, and Dr. B.R. Ambedkar Park, promoting green spaces for residents.
Awards and Achievements:
The corporation has earned several accolades, including the National Urban Water Award (2009) and recognition for its Siti e-Governance Project.
Pollution Control and Sustainability
Vijayawada is part of the Solar/Green Cities initiative by the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy, supporting eco-friendly development.
- Public Transport:
- The APSRTC introduced CNG-fueled buses to lower pollution levels. While these are gradually being replaced by BS4/BS6 diesel-fueled buses, APSRTC is investing in electric and biodiesel buses for sustainable mobility.
- Many CNG auto-rickshaws operate in the city. Recently, electric auto-rickshaws have been introduced to enhance environmentally friendly transportation.
Law and Order
The Vijayawada City Police Commissionerate ensures law and order in an area covering 1,211.16 square kilometers (467.63 square miles).
- Led by the Police Commissioner of the Additional Director General of Police rank, the force comprises a Joint Commissioner and four Deputy Commissioners of Police (IPS officers).
- The current Police Commissioner is Bathini Sreenivasulu.
Dedicated divisions and modern surveillance systems bolster the city’s safety and crime prevention efforts.
Economy of Vijayawada
Vijayawada is recognized as one of India’s fastest-growing urban economies, with a robust GDP of $11.292 billion as of 2020. The city’s economy spans across construction, education, entertainment, food processing, hospitality, transportation, and related services. Classified as a Y-grade city under the Sixth Central Pay Commission, Vijayawada is strategically positioned as a thriving hub for commerce and industry.
Economic Growth and Future Projections
- In 2010, Vijayawada’s GDP was estimated at $3 billion (₹18,000 crore), and predictions indicated it could reach $17 billion (₹1,02,000 crore) by 2025.
- According to an Oxford study, the city’s GDP, valued at $5.8 billion in 2018, is expected to grow to $21 billion by 2035.
This exponential growth is attributed to Vijayawada’s dynamic trading landscape, burgeoning IT infrastructure, and strategic focus on development.
Major Economic Drivers
- Agriculture and Trade
Vijayawada’s agrarian roots play a significant role in its economy. The Nunna Mango Market, one of Asia’s largest mango trading hubs, serves as a major export center, connecting the city to large domestic markets.Vijayawada is also central to petroleum logistics, with major companies such as BPCL, HPCL, and IOCL managing bottling, storage, and transportation from the city. - Industry and Manufacturing
- Vijayawada has been at the forefront of industrial development in Andhra Pradesh.
- The state’s first cement factory, Andhra Cements (1937), was established here, followed by Siris Pharmaceuticals, Andhra’s first pharma company (1950).
- IT and Technology
- Vijayawada is rapidly emerging as a major IT hub.
- HCL Technologies and Wipro are setting up significant facilities near Gannavaram, providing employment to thousands.
- Two major IT parks—one in Gannavaram and another in Mangalagiri—host prominent companies like Tech Mahindra, HCL, PI Data Center, VSoft, Efftronics, KJ Systems, and EPSoft.
- The city is fast becoming a preferred tier-2 destination for IT/ITES services.
- Real Estate Development
As the population and economic activity increase, Vijayawada’s real estate prices are soaring. The city is witnessing extensive urban expansion fueled by investments in IT, industrial, and entertainment infrastructure.
Specialized Infrastructure
- APIIC Mega Food Park: Located in Mallavalli, near Gannavaram, this facility caters to food processing industries, enhancing Vijayawada’s role as a food export hub.
- Cyber Security Office: Managed by Tech Mahindra, it underscores the city’s commitment to securing its growing digital economy.
- Amusement Parks: Wonderla plans to invest ₹250 crore in developing a 50-acre amusement park between Vijayawada and Guntur, promising to bolster tourism and recreation.
Investment and International Presence
Vijayawada continues to attract international companies due to its favorable location and economic incentives. It is set to play a major role in India’s technology-driven economy, with facilities capable of employing thousands of local talent and serving global markets.
Culture of Vijayawada
Vijayawada is celebrated as a city rich in culture, tradition, and heritage, offering a blend of ancient practices and contemporary lifestyles. Residents, often referred to as Vijayawada’s, uphold a vibrant cultural legacy marked by festivals, handicrafts, and religious diversity.
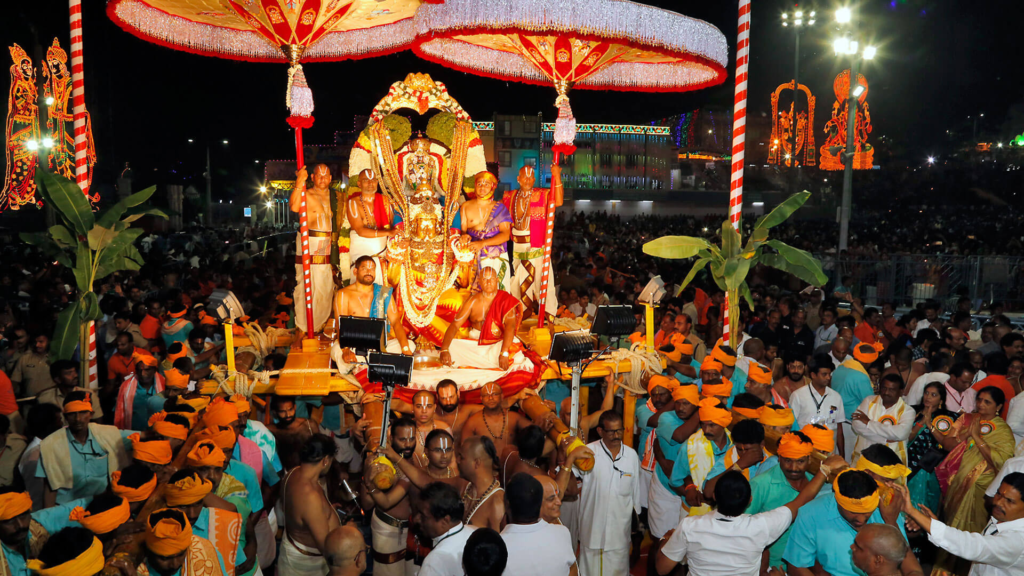

Art and Craft
One of the city’s most iconic contributions to Indian culture is the Kondapalli toys. These handcrafted wooden toys, made in the suburb of Kondapalli, represent the artistic skills passed down generations. With themes often revolving around rural life, mythology, and festivals, Kondapalli toys have gained recognition across India and abroad.

Festivals and Religious Harmony
Vijayawada is a mosaic of religious communities, and this diversity is mirrored in its festivals and rituals.
- Hindu Festivals
- The city is most famous for the Dussera festival, celebrated with grandeur at the Kanaka Durga Temple, a shrine dedicated to Goddess Durga.
- A special feature of the celebration is the Theppotsavam (boat festival) on the Krishna River.
- Islamic Heritage
- The Hazarat Bal Mosque, a prominent Muslim shrine in the city, houses a relic believed to belong to the Prophet Mohammed.
- Devotees from various parts of the country visit the shrine, which symbolizes Vijayawada’s multi-religious ethos.
- Christian Landmarks
- The Gunadala Matha Shrine stands as an important Christian pilgrimage site. Its annual festival (February 9-11) and the illumination on Christmas Eve attract thousands of devotees.
Community Events
- The Vijayawada Municipal Corporation organizes “Happy Sunday” on the first Sunday of every month at M.G. Road. This initiative brings citizens together for sports, games, cultural performances, and yoga, fostering a strong sense of community.
- These events help promote urban well-being and give artists and performers a platform to showcase their talent.
Cultural Identity in Clothing
- Traditional wear remains a stronghold in Vijayawada’s culture, with men typically wearing dhotis and women in sarees or salwar kameez for festive or traditional occasions.
- However, like most urban centers, western attire is widely accepted and commonly worn, especially among the younger population.
Key Cultural Landmarks
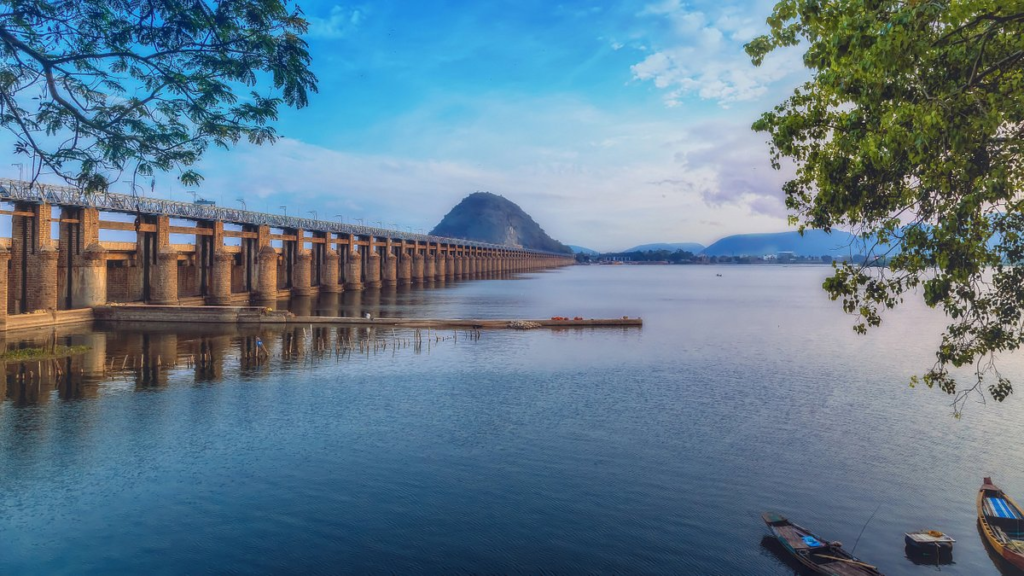
- Kanaka Durga Temple: Situated atop the Indrakeeladri Hill overlooking the Krishna River, it is one of the most revered temples in Andhra Pradesh.

- Prakasam Barrage: An iconic structure that reflects both the city’s cultural and engineering achievements, often lit up beautifully at night.

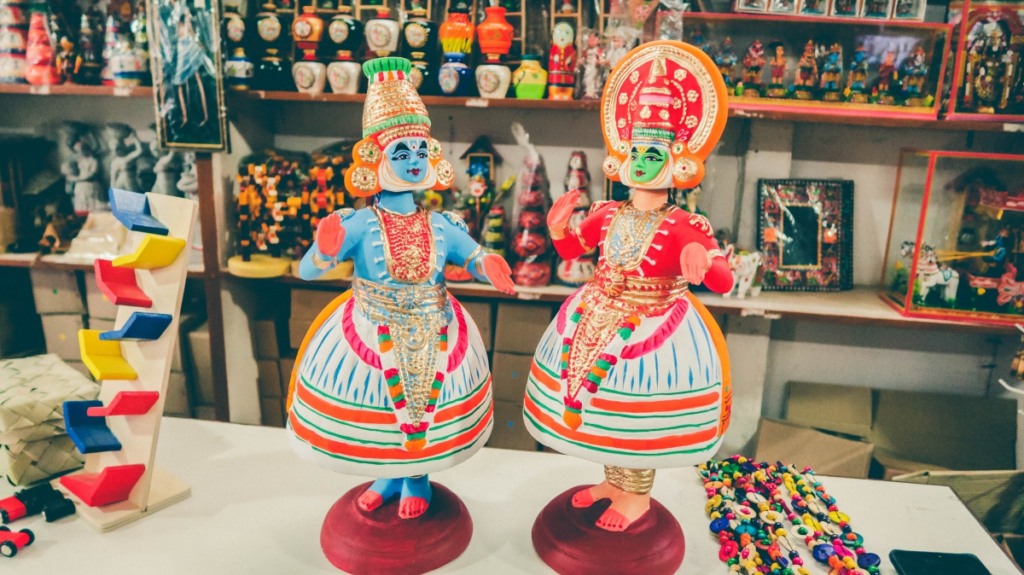
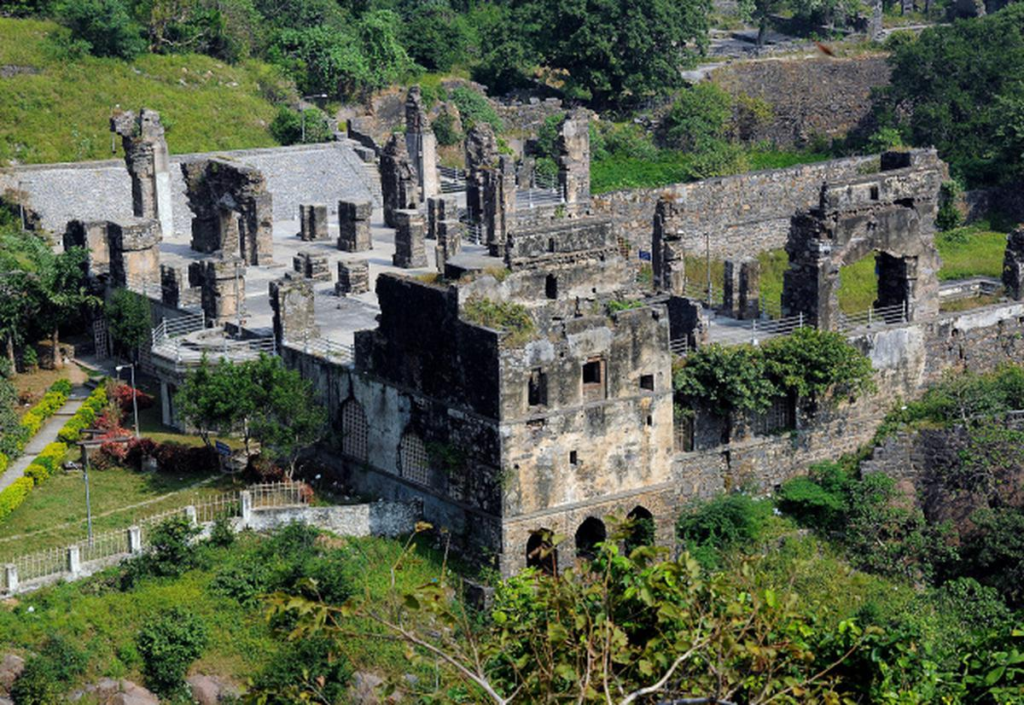
- Kondapalli Fort: Beyond its historical significance, it represents Vijayawada’s heritage and cultural roots.

Arts, Crafts, and Artefacts of Vijayawada
Vijayawada is a hub of artistic heritage and craftsmanship, celebrating its cultural richness through a range of art forms, crafts, and historical artefacts. From the globally recognized Kondapalli Toys to the archaeological treasures preserved in its museums, the city exemplifies Andhra Pradesh’s dedication to preserving its traditional and cultural essence.
Promoting Telugu Arts
The Vijayawada Art Society serves as a major institution for promoting Telugu art forms. Events like Poetic Prism 2015, a multilingual poetry meet, showcase Vijayawada’s contribution to literature and creative expression. Collaborating with organizations such as the Cultural Centre of Vijayawada, these platforms bring together local and international artists and writers, providing a space for dialogue and innovation in the arts.
Kondapalli Toys: A Symbol of Artisanal Skill
The Kondapalli Toys, or Kondapalli Bommalu, stand as one of the city’s most iconic cultural exports.
- These toys were granted Geographical Indication (GI) status in 2007, marking their historical and cultural significance.
- The toys are made from soft “Tella Poniki” wood, which is light and easy to carve, enabling intricate designs.
- Vibrant and eye-catching, these toys are painted with natural dyes, ensuring they are safe, non-toxic, and child-friendly.
Historical Origins:
The Kondapalli artisan community, believed to be the descendants of Rajasthani artisans of the 16th century, are known as Aryakhastriyas. Over centuries, they refined the craft, transforming their skill into a globally recognized art form.
Themes often depicted include rural life, mythology, festivals, and cultural vignettes, offering a glimpse into India’s diverse traditions.
Archaeological Relics and Museums
- Victoria Jubilee Museum
- Located in Vijayawada, this archaeological museum is a repository of cultural treasures.
- It houses Buddhist and Hindu relics, sculptures, paintings, and artefacts dating back to the 2nd and 3rd centuries, making it a must-visit for history enthusiasts.

- Key Highlights
- Rare sculptures portraying historical religious practices.
- Artefacts that reflect the Buddhist and Hindu cultural influence on Vijayawada’s evolution as a major spiritual and trade center in southern India.
Transport Infrastructure of Vijayawada
Vijayawada boasts a well-established and evolving transportation network, positioning itself as a critical connectivity hub for both local and interstate travel in southern India. Its blend of traditional and modern transport options ensures seamless movement within and outside the city, catering to its growing population and economic dynamism.
Public Transport: Serving Local Commuters
The primary modes of intra-city public transport in Vijayawada include city buses and auto-rickshaws, supplemented by motorcycles, bicycles, and cycle rickshaws.
- APSRTC (Andhra Pradesh State Road Transport Corporation):
- Operates approximately 450 buses daily, accommodating nearly 300,000 passengers.
- Key stations:
- Pandit Nehru Bus Station: Among the largest and busiest bus terminals in India, also serves as the APSRTC headquarters.
- Autonagar Bus Terminus and City Bus Port: Used primarily for city bus services.
- Major Routes: City buses operate along MG Road, Besant Road, and Eluru Road, extending to outer regions like Mangalagiri, Gannavaram, and Kondapalli.
- Auto-rickshaws remain an essential mode of short-distance travel, with notable initiatives like the women-driven “She Autos” enhancing inclusivity and safety.
Discontinued BRTS Corridor
Despite its advanced infrastructure with an investment of ₹150 crore (US$18 million), the Bus Rapid Transit System (BRTS) corridor was discontinued in 2016 due to poor commuter response.
Road Infrastructure: Expanding Regional and National Connectivity
Vijayawada enjoys robust connectivity through National Highways and arterial roads.
- Major National Highways:
- NH-16: Connects Kolkata to Chennai, traversing through Vijayawada, creating a vital link to key cities.
- NH-65: Links Pune, Hyderabad, and Machilipatnam.
- NH-30: Terminates at Ibrahimpatnam, enhancing links with Chhattisgarh.
- Arterial Roads and Bridges:
- The city features 16 bridges that ensure smooth traffic across canals like Bandar, Eluru, and Ryves.
- Roads such as MG Road (Bandar Road) and Eluru Road serve as lifelines, accommodating up to 90,000 vehicles daily.
- The total road length of 1,264 km is shared by municipal roads, highways, and departmental roads.
- Key Traffic Junctions:
- Benz Circle: The busiest intersection, managing around 57,000 vehicles daily where NH-16 and NH-65 meet.
Golden Mile Project: India’s First Smart Street
A standout innovation in Vijayawada’s transport network is the Golden Mile Project, a pioneering initiative under the Smart City Mission. Spanning a 2.9 km stretch of MG Road, the project aims to improve urban living through smart technologies.
- Facilities and Features:
- Free Wi-Fi, digital kiosks, and smart parking systems.
- Intelligent street lighting and motion sensors for traffic management.
- Surveillance cameras (101 units), with live traffic monitoring and density calculations.
- Sustainability and Efficiency:
- 240 solar-powered lights and parking sensors reduce congestion.
- Real-time city monitoring at the municipal headquarters for improved governance.
- Total investment: ₹7.83 crore, jointly funded by Cisco Systems, Vijayawada Municipal Corporation, and Andhra Pradesh Urban Finance & Infrastructure Development Corporation.
Future-Proofing Transportation in Vijayawada
With rising vehicle density and rapid urban growth, Vijayawada is consistently upgrading its transportation infrastructure. Efforts like expanding highway access, encouraging eco-friendly transport solutions, and leveraging smart city technologies are crucial for meeting the city’s evolving demands. The balanced integration of traditional and advanced systems underscores its role as an essential regional connectivity hub.
Rail and Air Connectivity in Vijayawada
Vijayawada serves as a pivotal hub for both rail and air transport, offering comprehensive connectivity across India and beyond. The city’s strategic positioning and well-established infrastructure ensure smooth travel, whether on land or in the air.
Rail Transport: A Crucial Hub in South India
Vijayawada Junction Railway Station stands out as a prominent landmark in Indian Railways’ network, with a rich history and impressive functionality.
- Historical Significance:
- Established in 1888, it played a vital role in connecting the region to the country’s railway system.
- By 1889, Vijayawada had its first railway connection to Hyderabad, marking its emergence as a connectivity hub.
- Current Importance:
- Classified as a Non-Suburban Grade-2 (NSG-2) station under the Vijayawada railway division, it is among the busiest railway stations in South India.
- The station links key locations such as Hyderabad, Chennai Central, Visakhapatnam, and Machilipatnam.
- Houses diesel and electric loco sheds, maintaining a capacity for 220 locomotives combined.
- Suburban and Satellite Stations:
- Suburban rail services connect Vijayawada with Guntur and Tenali.
- Vijayawada’s satellite stations include:
- Gannavaram, Gunadala, Krishna Canal, Ramavarappadu.
- Kondapalli, Rayanapadu, Madhura Nagar, and Nidamanuru.
Future Rail Developments
- A proposed circular train network aims to connect Vijayawada with nearby cities like Eluru, Guntur, Tenali, Mangalagiri, and the state capital Amaravati.
- Plans for a 66 km light transit system under the Andhra Pradesh Metro Rail Corporation Ltd (APMRC) would enhance mobility within and around Vijayawada, establishing critical links with Amaravati and surrounding suburbs.
Air Transport: A Gateway to the World
Vijayawada Airport, located in Gannavaram, bridges the region to the country’s major metropolitan cities and international destinations.
- Transformation into an International Hub:
- The airport was upgraded from a domestic facility to an international airport on 3 May 2017.
- Although international flights started to Singapore in 2018 via Indigo Airlines, these were discontinued in June 2019 due to the cessation of Viability Gap Funding by the state government.
- Domestic Connectivity and Growth:
- Airlines such as Air India, Jet Airways, and SpiceJet operate regular flights.
- Passenger and aircraft movements have seen significant growth, with 70% growth in passenger movement and 65% growth in aircraft movement recorded in FY 2019.
- The airport catered to nearly 1.2 million passengers in FY 2019.
Future Prospects
- Despite challenges in international operations, Vijayawada Airport’s focus remains on increasing domestic connectivity and elevating passenger experiences through infrastructural upgrades.
Media in Vijayawada: A Vibrant Hub of Communication
Vijayawada has a rich and diverse media landscape that spans across print, radio, and television, serving as a vital information gateway for residents and the wider region. The city’s media outlets play a significant role in shaping public opinion and providing news, entertainment, and education to millions of people.
Print Media
Vijayawada’s media history dates back to its pioneering role in newspaper publication, beginning with the Visalaandhra, the first-ever newspaper in the state. Since then, the city has grown as a major center for both Telugu and English publications. Some of the most widely read Telugu newspapers published from Vijayawada include:
- Andhra Jyothy
- Eenadu
- Sakshi
- Suryaa
- Andhra Prabha
- Vaartha
- Prajasakti
- Udaya Bharatam
These publications are key players in regional news, providing comprehensive coverage of local, national, and international events. Vijayawada is also home to several prominent English-language newspapers, such as:
- Deccan Chronicle
- The Hindu
- The Times of India
- The Hans India
- News Boom
- The Fourth Voice
- Views Observer
These English dailies provide national and international perspectives, complementing the city’s Telugu publications.
Broadcast Media
Vijayawada has a significant presence in radio broadcasting as well. The city was home to the establishment of All India Radio Vijayawada, which commenced operations on 1 December 1948. This station holds special importance as it was named after Pingali Venkayya, the designer of the Indian national flag.
- All India Radio Vijayawada broadcasts several stations, including:
- Rainbow Krishnaveni FM
- Vividh Bharati
The presence of Doordarshan also plays a vital role in the city’s media outreach. Telugu Doordarshan Saptagiri is located in Vijayawada and provides quality programming, ranging from entertainment to educational content.
These media outlets offer a mix of cultural, news, and entertainment content to cater to the diverse interests of their audience.
Sports in Vijayawada: A Hub of Competitive and Recreational Sports
Vijayawada has an active sports culture, with numerous stadiums and facilities catering to both competitive athletes and recreational sports enthusiasts. The city has earned a name for hosting various national and international sports events, providing top-notch infrastructure for cricket, badminton, tennis, and more.
Key Sporting Venues
- Indira Gandhi Stadium
Located in the heart of the city, Indira Gandhi Stadium is a major sports complex and also serves as the headquarters for the Sports Authority of Andhra Pradesh. It has gained recognition for hosting several high-profile events, including its only Men’s One Day International (ODI) on 24 November 2002, when India played against the West Indies. The stadium also hosted the 1997 Women’s Cricket World Cup, where it saw a Women’s ODI match between England Women’s and Pakistan Women’s.

- Makineni Basavapunnaiah Stadium
Situated at Ajit Singh Nagar, Makineni Basavapunnaiah Stadium serves the northern part of the city. This open stadium has facilities for multiple sports and plays a significant role in the city’s sporting activities. - Indoor Stadiums
- Dandamudi Rajagopala Rao Indoor Stadium (DRRIS): Named after the Olympic-level weightlifter, Dandamudi Rajagopala Rao, this stadium is one of the top indoor sports venues in Vijayawada. It has hosted prestigious events such as the 79th Senior Badminton Championships, along with many other national-level sporting events.
- Chennupati Ramakotaiah Indoor Stadium (CRIS): Located at Patamatalanka, this indoor stadium further enhances the city’s ability to host indoor sports tournaments.
Upcoming and Additional Venues
- Andhra Cricket Association (ACA) International Cricket Stadium
The ACA International Cricket Stadium, under construction in Navuluru village near Mangalagiri, is set to become a major sporting venue in the region. With plans for a 30-acre site, it will enhance the city’s reputation as a cricketing hub and host international matches once completed. - Vijaya Madhavi Tennis Academy
Located in Loyola College, the Vijaya Madhavi Tennis Academy offers tennis coaching and hosts national-level tennis competitions. It remains one of the top tennis venues in the city.

- Railway Sports Stadium
Situated near the railway station, the Railway Sports Stadium is a key venue for various national-level competitions, including bodybuilding championships, Under-19 cricket, and other sports. With a seating capacity of 10,000, it is one of the largest stadiums in Vijayawada.
Other Sports Activities
Vijayawada’s sports infrastructure also includes various open and indoor facilities catering to different sports. Makineni Basava Punnaiah Stadium and Dandamudi Rajagopala Rao Indoor Stadium stand out as important venues for badminton, hosting national championships and developing local talent.
Overall, Vijayawada’s sporting culture continues to thrive, with multiple venues dedicated to nurturing talent and encouraging recreational participation across various disciplines. From major cricket events at Indira Gandhi Stadium to the city’s ever-growing indoor sports scene, the sports community in Vijayawada is poised for continued growth and development.
Awards and Recognition: Vijayawada’s Achievements
Vijayawada has gained significant recognition for its efforts in cleanliness and waste management, with the city receiving a prominent position in national rankings.
Swachh Survekshan 2021
In the Swachh Survekshan 2021, an annual cleanliness survey conducted by the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs, Vijayawada was ranked as the third cleanest city in India among cities with a population exceeding 10 lakh. The city’s rise from sixth place in 2020 to third place in 2021 was a noteworthy achievement and was driven by significant efforts in urban sanitation. The five-star “Garbage Free City” designation is another accolade that underscores the city’s commitment to cleanliness. Much of this success can be attributed to the policies of N. Chandrababu Naidu, who introduced modern waste disposal vehicles that revolutionized the way the city manages its waste.
Notable People from Vijayawada
Vijayawada, known for its vibrant culture and history, has produced many remarkable individuals who have made their mark in various fields.
- Nadeem Baig – Renowned Pakistani actor, singer, and producer, known for his contributions to the entertainment industry in Pakistan.
- Siva S. Banda – An Indian American aerospace engineer who has earned significant accolades in his field.
- Saraswathi Gora – A pioneering Indian social activist and leader of the Atheist Centre, fighting for social equality and progress.
- Koneru Humpy – Women’s World Rapid Chess Champion, one of the best chess players in the world.
- Lavanam – A prominent social reformer and Gandhian, known for his leadership in advocating for social change.
- Prasad Murella – Indian film cinematographer known for his contributions to the film industry.
- Rampilla Narasayamma – An Indian freedom fighter who played a pivotal role in India’s fight for independence.
- Teja Nidamanuru – An Indian-born cricketer who plays for the Netherlands national cricket team.
- Dandamudi Rajagopal – An Olympic weightlifter, famous for his exceptional accomplishments in weightlifting.
- Vangaveeti Mohana Ranga – A politician from Vijayawada, known for his involvement in the political scene of Andhra Pradesh.
- Ayyadevara Kaleswara Rao – Indian freedom fighter and the first Speaker of the Legislative Assembly of Andhra Pradesh.
- Goparaju Ramachandra Rao – The founder of the Atheist Centre, advocating for rational thinking and secularism.
- Kanuri Lakshmana Rao – A three-time Member of Parliament (MP) from Vijayawada and the Chief Engineer of Nagarjuna Sagar Dam.
- N. T. Rama Rao – A legendary Telugu film actor and the founder of Telugu Desam Party (TDP), one of the most significant political movements in the region.
- Akkineni Nageswara Rao – A celebrated Telugu film actor and founder of Annapurna Studios, an iconic production house.
- Viswanatha Satyanarayana – A revered Telugu writer who was awarded the Jnanpith Award in 1970, becoming the first recipient of the prestigious award for a Telugu author, along with the Padma Bhushan in 1971.
- Puchalapalli Sundarayya – A founding member of the Communist Party (Marxist) and a former Member of Legislative Assembly (MLA) from Vijayawada.
- Pingali Venkayya – The creator of the National Flag of India, a monumental figure in the country’s history.
These individuals have not only made notable contributions in their respective fields but also helped shape the cultural, social, political, and intellectual landscapes of both Vijayawada and the broader region of Andhra Pradesh.